Price wars amid heated bets: is China’s herpes zoster vaccine gold rush cooling off?
Another major vaccine product category is showing signs of cooling off.
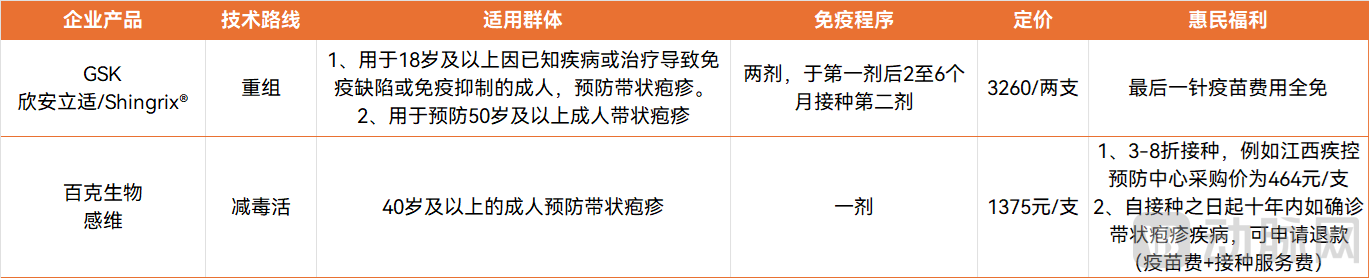
Recently, disease control and prevention centers across China have rolled out subsidized vaccination initiatives for herpes zoster. Two approved herpes zoster vaccines in China have undergone significant price reductions: the second dose of GSK's imported recombinant herpes zoster vaccine (brand name: Shingrix®) is now offered free of charge, while the domestic herpes zoster live attenuated vaccine produced by BCHT (brand name: Gan Wei) is available at a discount of 30% to 80%.
The herpes zoster vaccine ranks among the top ten best-selling vaccine products globally. Since its global launch in 2018, Shingrix® has generated sales revenue exceeding 100 billion RMB. With a protective efficacy of over 90%, the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine Shingrix represents a significant advance over live attenuated vaccines. Its global sales exceeded 4 billion U.S. dollars in 2024.
In the Chinese market, however, the herpes zoster vaccine has not experienced such rapid growth. The early sales of herpes zoster vaccines in China once showed remarkable momentum. GSK's Shingrix®, launched in China in 2020, achieved sales of 600 million RMB in 2021 and exceeded 1.2 billion RMB in 2022. BCHT's live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine, approved in 2023, recorded sales of 880 million RMB in its first nine months on the market.
By 2024, however, market growth began to slow. GSK's financial reports noted a decline in Shingrix® sales in China, while BCHT's live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine saw its sales drop to 250 million RMB in 2024.
While demand for herpes zoster vaccines has shown signs of contraction, the supply side continues to attract numerous entrants. Over 30 herpes zoster vaccine candidates are currently awaiting approval for market launch in China. According to industry insiders, the development and commercialization of a single herpes zoster vaccine require an investment of several billion RMB. Can the herpes zoster vaccines, on which Chinese companies have placed heavy bets, regain their momentum?
More than 30 companies have invested in the development of herpes zoster vaccines, primarily driven by their significant clinical value in preventing the highly distressing course of the disease.
Herpes zoster is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which lies dormant in the body and is the same virus responsible for chickenpox. Reactivation typically occurs when an individual's immunity to VZV weakens due to factors such as aging or immunosuppression, predominantly affecting older adults. Symptoms of the disease include pain, general malaise, fever, chills, muscle aches, headaches, itching, numbness, and a distinctive rash. After recovery from herpes zoster, the virus may remain inactive in the dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerve ganglia for extended periods, potentially lasting decades.

Image Source: Tencent Medical Dictionary
This disease, with pain levels reaching up to a severity of ten, is not uncommon among middle-aged and older adults. According to data from Luzhu Biotechnology's prospectus, among individuals aged 50 and above in 2021, the number of new herpes zoster cases reached 3.9 million in China, 1.1 million in the United States, and 2 million in Europe.
Thanks to its over 90% protective efficacy, the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine became a blockbuster after approval. Approved in the United States in October 2017, Shingrix® quickly replaced older products due to its high efficacy and is currently the only commercially available herpes zoster vaccine in the U.S. Following its approval, the vaccination rate among Americans aged 50 and above increased from 0.1% in 2017 to 26.8% in 2021. The market size for herpes zoster vaccines also stabilized at approximately $1.7 billion.
In China, however, since the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine was approved in 2020, data show that as of September 2024, the vaccination rate among adults aged 40 and above in 25 provinces was only 0.79%.
Why has the herpes zoster vaccine failed to gain traction in the Chinese market? Industry analysts attribute this to three major factors limiting its market expansion in China:
First, the high cost has dampened vaccination willingness among the elderly. Currently, the domestic live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine (produced by BCHT) is priced at approximately 1,375 RMB per dose, while the imported recombinant herpes zoster vaccine (GSK) costs around 3,260 RMB for two doses. As the vaccine has not yet been included in the national immunization program, recipients must pay the full amount out-of-pocket, creating a significant financial burden for elderly individuals with limited purchasing power. In contrast, Shingrix® in the U.S. is priced at about $120 per dose. It is covered under Medicare Part D, substantially reducing the financial burden for patients, while Medicaid covers Shingrix® vaccination for individuals aged 50 and above in approximately two-thirds of U.S. states, significantly lowering the access barrier.
Second, awareness of herpes zoster and its vaccine remains insufficient among the elderly. Despite ongoing public health education efforts by companies and institutions, effectively reaching the elderly demographic remains challenging. To address this gap, some companies have positioned the herpes zoster vaccine as a "filial piety vaccine," targeting younger individuals with stronger awareness and higher purchasing power to encourage vaccination for their elderly relatives. While this strategy initially boosted vaccine awareness, overall knowledge levels still require improvement.
Additionally, in the United States, vaccination is highly convenient. Shingrix is widely available at major chain pharmacies, clinics, and hospitals, including CVS Pharmacy, Walgreens, and Walmart, offering accessible vaccination services.
In essence, Shingrix®'s rapid U.S. penetration and global blockbuster status were fueled by its market exclusivity driven by outstanding immunogenicity, comprehensive insurance coverage, and convenient vaccination access. Conversely, the stalled growth in China stems from factors such as limited disease awareness, constrained purchasing power among the elderly, and evolving product competition.
The market growth rate for the herpes zoster vaccine segment has already slowed down, yet new entrants continue to emerge on the supply side. In China, there are more than 30 candidate herpes zoster vaccine products awaiting approval for market launch.
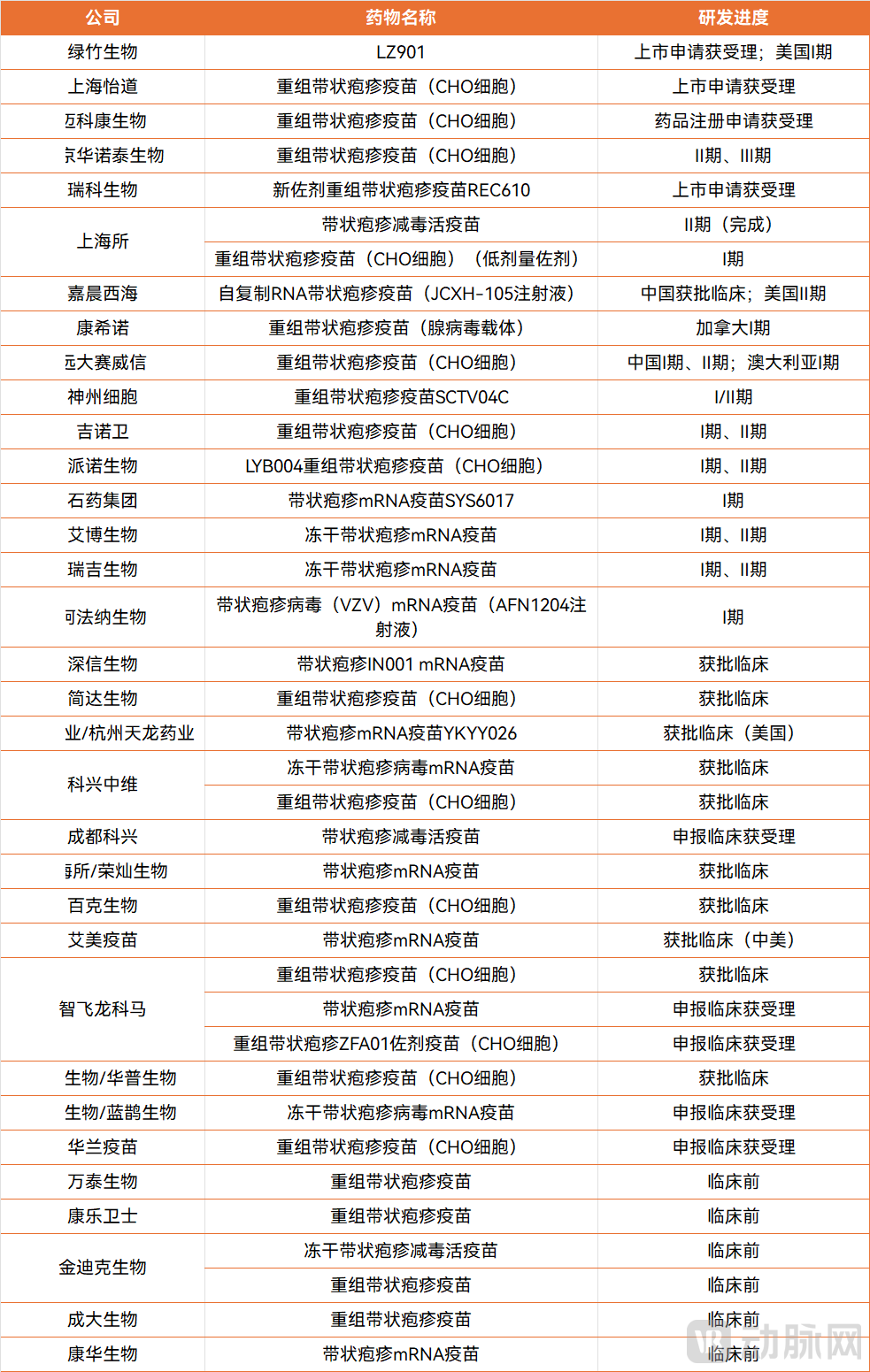
Clinical Progress of Herpes Zoster Vaccines in China (Data sourced from the internet; if there are any omissions, please feel free to contact us for corrections) Data source: Drug Times
The involvement of over 30 Chinese companies in this field follows underlying industry dynamics. The relatively manageable technical barriers, strategic positioning within the elderly vaccine portfolio, and the combined influence of Shingrix's success and capital investment have collectively driven this wave of engagement.
Industry insiders offer the following analysis: "Firstly, from the perspectives of R&D technology and cost-efficiency, the antigen design and cell line construction for the herpes zoster vaccine are relatively straightforward, with the key challenge lying in the selection of an appropriate adjuvant. Additionally, the recombinant herpes zoster vaccine utilizes CHO cell lines, similar to those employed in antibody drug production. China possesses a mature CDMO industrial chain capable of providing related outsourcing services, thereby lowering the entry barrier for companies.
Secondly, from a strategic standpoint, some companies have already established portfolios of vaccines targeting the elderly, such as the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine and the quadrivalent influenza vaccine. Including the herpes zoster vaccine in their product lineup allows them to leverage existing channels for synergistic growth."
Thirdly, the commercial success of GSK's Shingrix has created a powerful demonstration effect. As the leading product in the herpes zoster vaccine market, Shingrix has generated cumulative sales exceeding 100 billion RMB since its global launch in 2018, with annual peak sales surpassing $4 billion. This high-return prospect has attracted significant capital and a surge of startups into the field, leading to rapid expansion of the product pipeline.
From a technical standpoint, Chinese companies primarily focus on recombinant protein and mRNA technology platforms. The live attenuated vaccine route has seen some companies opting out. For instance, Wantai BioPharm strategically discontinued the development of its live attenuated herpes zoster vaccine after Phase II clinical trial results indicated that its protective efficacy was inferior to that of Shingrix®.
The two key competitive advantages of Chinese domestic candidate vaccines are better tolerability and more competitive pricing. Currently, most recipients of the approved recombinant herpes zoster vaccine Shingrix® in China experience transient or prolonged nodules at the injection site, along with injection site pain.
Chinese companies are working to reduce adverse reactions associated with herpes zoster vaccination through innovations in vaccine adjuvants. For example, Luzhu Biotechnology and Maxvax are among the clinical frontrunners in this area. Luzhu Biotechnology's LZ901 employs a different antigen structure and adjuvant formulation compared to Shingrix®. The aluminum hydroxide adjuvant used in LZ901 is expected to result in a lower incidence of adverse reactions compared to the oil-based adjuvant used in Shingrix®. Clinical data from Luzhu Biotechnology's head-to-head study showed that, compared to the HZ/su vaccine (Shingrix®), LZ901 induced superior cellular immunogenicity and demonstrated better safety in adults aged 50 or above. Meanwhile, Maxvax's recombinant herpes zoster vaccine utilizes a recombinant VZV glycoprotein E expressed in CHO cells and the company's proprietary MA105 adjuvant system.
Globally, reducing vaccination-related reactions through adjuvant innovation is also a key focus for industry leaders. In December 2025, Sanofi announced the acquisition of Dynavax Technologies Corporation, whose pipeline includes an investigational herpes zoster vaccine. Dynavax's candidate, Z-1018, demonstrated immunogenicity comparable to Shingrix in preliminary clinical studies, with equivalent antibody and CD4 T-cell immune responses. Moreover, due to its proprietary CpG-1018 adjuvant, Z-1018 exhibited significantly better tolerability than Shingrix.
In terms of pricing, domestically produced recombinant herpes zoster vaccines in China are expected to be priced lower than Shingrix®. Data from Luzhu Biotechnology's prospectus indicate that LZ901 is projected to be priced at approximately RMB 500 to RMB 800 per dose.
According to the Ministry of Civil Affairs of the People's Republic of China, by the end of 2024, China's population aged 60 and above reached 310 million, accounting for 22% of the total population. As public awareness of herpes zoster and its risks continues to grow, the acceptance of China-produced recombinant herpes zoster vaccines is steadily increasing. Despite the vast potential target population, vaccination rates for herpes zoster remain relatively low, indicating significant market opportunities.
With better tolerability, lower pricing, and high protective efficacy, China-developed recombinant herpes zoster vaccines are expected to capture a portion of the market upon approval.
Overall, whether for the HPV 9-valent vaccine or the herpes zoster vaccine, the Chinese market has followed a trajectory of initial enthusiasm followed by a slowdown. The success seen in the U.S. market is not easily replicable: the U.S. industry is highly concentrated, dominated by a few giants such as Pfizer, GSK, MSD, and Sanofi, and is characterized by single-product-driven growth—leading innovative products quickly gain insurance coverage and achieve widespread adoption, leading to rapid market expansion and replacement of outdated products, after which the market stabilizes. In contrast, the Chinese market features more participants and a more fragmented landscape, leaving limited incremental opportunities for latecomers.
This places higher demands on Chinese companies. To achieve sustainable growth in a fragmented and highly competitive market, products must not only be launched swiftly but also demonstrate differentiated innovation and robust commercialization capabilities.
