The nuclear medicine CXO services market: rising on the wave
Nuclear medicine has recently become a major focus in the pharmaceutical field, particularly with radiopharmaceuticals, where Radionuclide-Drug Conjugates (RDCs) have emerged as a leading frontier.
Novartis' Pluvicto, a key nuclear medicine product, generated sales of $1.392 billion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 42%. In the first three quarters of 2025, its revenue reached $1.389 billion, nearly matching its full-year 2024 sales and representing a 33% growth. At the 2025 J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference, Novartis projected that Pluvicto's peak sales are expected to exceed $5 billion.
Despite the robust sales of Pluvicto, supply constraints have persisted. Novartis had to temporarily suspend the supply of Pluvicto to new patients, citing production capacity limitations and inability to meet surging demand. Production capacity has thus been a significant factor limiting the commercial scale-up of Novartis' nuclear medicine.
Currently, nuclear medicine companies are actively conducting research focused on major disease indications and novel therapeutic targets, as shared by Qiao Haitao, General Manager of C Ray Therapeutics (Chengdu), with VCBeat. As global R&D and commercialization of nuclear medicines continue to accelerate, related CXO (pharmaceutical contract outsourcing) services are also becoming increasingly active. According to data from InsightAce Analytic, the global market size for radiopharmaceutical CDMO (Contract Development and Manufacturing Organization) /CMO (Contract Manufacture Organization) services was $2.75 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $5.44 billion by 2031. The high growth prospects of the nuclear medicine CXO services market are attracting significant capital inflows into this field.
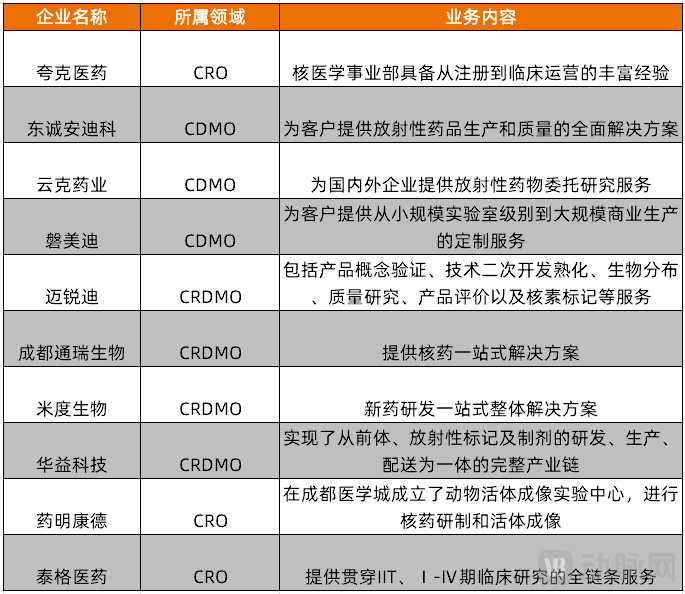
Figure 1. Chinese companies involved in the nuclear medicine CXO services business (Source: VCBeat, incomplete compilation)
Currently, various sources of capital, including MNCs (Multinational Corporations), CXO service providers, and nuclear medicine companies, are entering the radiopharmaceutical CXO services market , with business areas covering upstream CROs (Contract Research Organization) and downstream CDMOs.
1) MNCs Face Production Capacity Challenges
Nuclear medicine is a special class of pharmaceuticals that involves radionuclides in their production and use, subjecting them to stringent requirements throughout the lifecycle of the nuclides, including production, transportation, and administration.
Unlike conventional drugs that can be stored for extended periods, the radionuclides used in nuclear medicines have very short half-lives, resulting in a shelf life that may be only a few days. This poses significant challenges for manufacturing and distribution. Potential delays, such as customs inspections or shipping holdups, can render the drugs ineffective. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies must possess not only production capabilities but also robust distribution networks.
To overcome production bottlenecks and ensure supply chain security, MNCs are actively expanding their production capacities.
Novartis serves as a prime example. Previously, Novartis had to suspend the supply of Pluvicto to new patients due to insufficient capacity. To address this, Novartis has been continuously building nuclear medicine production capacity worldwide. In Europe, it has completed two radiopharmaceutical production sites in Ivrea, Italy, and Zaragoza, Spain. In the United States, its facilities in Millburn, New Jersey, and Indianapolis, Indiana, have also become operational, dedicated to supplying the U.S. market.
Furthermore, Novartis is constructing a radiopharmaceutical production base in Haiyan, Zhejiang, China, expected to commence operations by the end of 2026. Its Japanese subsidiary will invest $100 million to build a production facility in Sasayama, Japan. Available information indicates that Novartis will establish up to six global radiopharmaceutical production sites to support the commercial manufacturing and R&D needs of its nuclear medicines. Novartis has also indicated it may consider offering CDMO services once the production of its own RDCs stabilizes.
2) The Nuclear Medicine CXO Services Market Welcomes "New Players"
Beyond Novartis, other MNCs are also entering the nuclear medicine CDMO services market.
AstraZeneca has made strategic moves in nuclear medicine CDMO. In June 2024, Nucleus RadioPharma announced the completion of a Series A extension round financed by AstraZeneca. This investment followed AstraZeneca's $2.4 billion acquisition of Fusion Pharmaceuticals just three months earlier, marking another significant move in the radiopharmaceutical field. AstraZeneca's bet on Nucleus RadioPharma is based on the latter's comprehensive capabilities as a CDMO service provider, spanning R&D, production, manufacturing, supply, and clinical resources.
Sanofi is entering the nuclear medicine CDMO arena through partnerships. In September 2024, Sanofi entered into a licensing agreement with RadioMedix and Orano Med, focusing on the AlphaMedix (²¹²Pb-DOTAMTATE) project developed by RadioMedix. Under the agreement, Sanofi will be responsible for the global commercialization of the project, while Orano Med will handle the production of AlphaMedix through its global industrial platform.
Overall, MNCs are currently increasing their investments in the nuclear medicine CDMO sector, adopting a mix of strategies that include in-house capacity building, mergers and acquisitions, and strategic partnerships.
Recognizing the rapid growth momentum in the nuclear medicine field, established contract service organizations are also entering the sector, with companies like WuXi AppTec and Tigermed being representative examples.
WuXi AppTec has established an In-Vivo Imaging Center within the Chengdu Medical City, dedicated to nuclear medicine research and development and in-vivo imaging. The center currently utilizes 18 different radionuclides, including Yttrium-90 (⁹⁰Y), Technetium-99m (⁹⁹ᵐTc), Iodine-131 (¹³¹I), Lutetium-177 (¹⁷⁷Lu), and Actinium-225 (²²⁵Ac). The future scope of the center will encompass preclinical and certain clinical research services, catering to pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
Tigermed's team provides CRO services covering the entire spectrum from Investigator-Initiated Trials (IIT) to Phase I-IV clinical studies for nuclear medicine companies. Its service offerings include regulatory submissions, clinical development strategy, medical writing, medical monitoring, clinical operations, data management, and statistical analysis. Additionally, Tigermed offers supply chain support services such as customs clearance, transportation, and radionuclide distribution for nuclear medicines.

Figure 2. Tigermed Provides Full-Chain Services for Nuclear Medicine (Source: TigerMed Official Website)
In addition, Tigermed has also participated in the Series A investment of Bivision Pharmaceuticals, a radiopharmaceutical company, establishing closer commercial ties with downstream radiopharmaceutical enterprises through equity investment.
3) Active Expansion by Dedicated Radiopharmaceutical Companies
Beyond these new entrants, companies that specialize in the nuclear medicine field are also actively expanding their CXO service businesses.
The traditional industry leader, DC Pharma through its subsidiary MITRO Biotech provides CRDMO (Contract Research, Development, and Manufacturing Organization) services to both Chinese and international pharmaceutical companies.
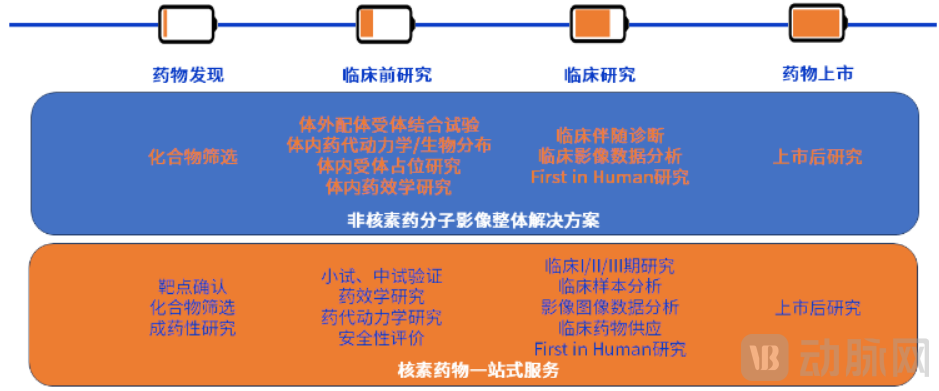
Figure 3. CRDMO Services for Nuclear Medicine Provided by MITRO Biotech (Source: DC Pharma Announcement)
MITRO Biotech offers nuclear medicine clients comprehensive, one-stop CRO services covering the entire process from pharmaceutical research, non-clinical studies, clinical research (Phase I-IV), to regulatory submissions. It also provides CDMO services for the clinical stage, including process transfer and process optimization. To date, MITRO Biotech has supported over 20 nuclear medicine products in obtaining clinical trial approvals.
Alongside established nuclear medicine companies, emerging players in the nuclear medicine CXO sector are also experiencing continuous growth.
Glotope Advanced Pharmaceutical, a one-stop CRO/CDMO platform under Sinotau Pharmaceutical, offers end-to-end services from early-stage R&D to commercial production. Glotope has established R&D platforms and production bases in Jiangsu, Guangdong, and Sichuan to flexibly support clients across different regions. The company has partnered with both Chinese and international nuclear medicine firms and has completed 23 radionuclide labeling projects to date.
C Ray Therapeutics provides comprehensive nuclear medicine solutions encompassing process development, quality studies, preclinical evaluation, IND application support, clinical drug supply, and commercial manufacturing, backed by a reliable and stable logistics system. C Ray Therapeutics is currently managing over 60 active CRDMO projects, delivering one-stop nuclear medicine services to global clients.
We observe that MNCs, CXO companies, and dedicated radiopharmaceutical companies are all increasing their investments in the nuclear medicine CXO sector. The sustained boom in nuclear medicine is fueling a high-growth phase for upstream CXO service providers.
Although the nuclear medicine CXO field is attracting more and more companies to participate, the uniqueness of nuclear medicine determines that CXO companies in this field need to possess distinctive advantages.
1) Stable Supply of Radionuclides
Radionuclides are essential for the therapeutic efficacy of nuclear medicines, making a stable supply a critical factor in evaluating the supply chain resilience of nuclear medicine CXO companies. Currently, commercial radionuclide supply in China is concentrated in two major regions: Sichuan and Zhejiang.
The Medical Isotope Production Base in Jiajiang, Sichuan, officially commenced operations at the end of 2024. This project, constructed by the China Nuclear Power Research & Design Institute, is located in Jiajiang County, Leshan City, Sichuan Province, and is supported by the nearby Jiajiang research reactor. The core facility is the Sichuan Haitong Isotopes Production Base. Following its launch, the base will achieve large-scale production of eight key radionuclides: Lutetium-177 (¹⁷⁷Lu), Yttrium-90 (⁹⁰Y), Radium-223 (²²³Ra), Iodine-125 (¹²⁵I), Phosphorus-32 (³²P), Rhenium-188 (¹⁸⁸Re), Holmium-166 (¹⁶⁶Ho), and Carbon-14 (¹⁴C), covering crucial diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
Previously, China faced a severe shortage of supply for radionuclides such as Lutetium-177 (used in diagnosing and treating diseases like prostate cancer) and Yttrium-90 (used in liver cancer treatment). The operationalization of the Sichuan Haitong base will increase the Chinese production rate of these isotopes, effectively alleviating the longstanding dependence on imports—a critical bottleneck issue—and holds the potential for future export.
The CNNC Qinshan Isotope Production Base is located in Haiyan, Zhejiang. This base is planned to house five production lines for Cobalt-60 (⁶⁰Co), Carbon-14 (¹⁴C), Lutetium-177 (¹⁷⁷Lu), Iodine-131 (¹³¹I), and Strontium-89 (⁸⁹Sr). Currently, Qinshan Nuclear Power has already achieved batch production of Cobalt-60, domestic supply of Carbon-14, and the market launch of its first batches of Lutetium-177.
Leveraging the commercial heavy-water reactor at the Qinshan Nuclear Power base, Lutetium-177 has achieved large-scale production. The planned annual irradiation production capacity for Lutetium-177 exceeds 10,000 curies, sufficient to meet the entire domestic demand in China.
Furthermore, nuclear medicine R&D companies are also beginning to engage in the upstream radionuclide sector through vertical integration strategies. A case in point is Chengdu New Radiomedicine Technology, which currently has four pipeline assets in clinical stages while also achieving independent preparation and supply capabilities for over 10 critical radionuclides, including Germanium-68 (⁶⁸Ge) and Actinium-225 (²²⁵Ac).
A stable Chinese radionuclide supply will effectively mitigate the previous heavy reliance on imports, providing essential resource security for nuclear medicine CXO companies in their R&D and production operations.
2) Stable Production Capability
Compared to conventional pharmaceuticals, nuclear medicines are unique as they involve the handling of radioactive sources. Consequently, the production process requires additional considerations for radiation protection and contamination control, as well as obtaining a radiation safety license from the competent regulatory authority.
From the perspective of production facilities, plant location must avoid residential areas. Building structures need to utilize radiation-shielding materials, and wall thickness must be customized according to standards corresponding to the specific types of isotopes used. Additionally, personnel must undergo radiation-specific training, and emergency decontamination procedures and protocols for handling dose exceedances must be established.
These hardware and software requirements are merely the foundation for nuclear medicine production. For nuclear medicine CDMOs, maintaining stable production capacity and achieving a product qualification rate that meets specifications are the keys to winning client trust.
Unlike other drug types, the radionuclides in nuclear medicines have half-lives; for instance, Lutetium-177 has a half-life of only 6.7 days. Therefore, the entire process from radionuclide acquisition to subsequent processing tests the CDMO's management capabilities. Any misstep could negate all prior efforts. If production capacity fails to meet requirements, downstream animal or human trials may be affected, potentially missing the optimal therapeutic window. Production delays or non-compliant products that prolong the production timeline can also diminish the therapeutic efficacy of the nuclear medicine.
Therefore, for nuclear medicine CDMOs, the entire business chain must operate with precision and high efficiency to achieve an exact match between production and demand. This requires not only compliant hardware and software facilities but also sufficient project experience and robust management capabilities as safeguards.
3) Distribution Capacity Assurance
Previously, purchasing radionuclides from other countries involved long lead times and high capital costs. Taking Lutetium-177 as an example, relying on imports required full payment months in advance, with supply being unstable. Furthermore, imports typically took around four days to arrive in China, posing significant pressure on supply chain security.
As radionuclides gradually achieve stable Chinese supply, nuclear medicine manufacturers are beginning to establish their operations around radionuclide production bases to maximize the efficiency of isotope distribution and ensure the needs of research and production are met. This has led to a trend of regionalized layout in nuclear medicine production.
Sichuan Haitong, leveraging the Jiajiang research reactor, has successfully achieved the production of multiple radionuclides, establishing a regional advantage in Sichuan. Currently, well-known companies including CNGT, Yunke Pharma, Grand Pharmaceutical Group, Chengdu New Radiomedicine Technology, and C Ray Therapeutics have formed a cluster in the Sichuan region.
Qinshan Nuclear Power, in collaboration with the Haiyan county government, has established the Haiyan Nuclear Technology Application (Isotope) Industrial Park. This park encompasses the entire industry chain, including isotope preparation, nuclear medicine production, and supporting services. Within the park, radionuclide products can be rapidly delivered to requesting companies. The stable supply chain assurance has attracted Novartis's nuclear medicine production project to Haiyan, which is expected to commence operations by the end of 2026.
Moreover, Qinshan Nuclear Power is located in the Yangtze River Delta region, allowing companies to leverage the area's convenient logistics to meet radionuclide demands in surrounding areas. DC AMS Pharma can provide clients with efficient nuclear medicine distribution services, as noted by a long-time professional in the regional nuclear medicine business interviewed by VCBeat. Currently, DC AMS Pharma has established over 30 nuclear medicine production and distribution centers across China, forming a nationwide networked industrial layout.
It is evident that the nuclear medicine CXO sector has special requirements across the entire chain—from radionuclide supply to production and distribution—thereby forming unique industry barriers. Precisely due to this specificity, one-stop nuclear medicine CRDMO providers hold a more distinct competitive advantage compared to nuclear medicine CXO firms involved in only a few segments of the chain, as shared by Qiao Haitao, General Manager of Chengdu Operations at C Ray Therapeutics, with VCBeat.
The advantages of one-stop service are specifically reflected in three aspects: cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and value enhancement.
From a cost perspective, access to radionuclides is a key factor in cost control for nuclear medicine CXO companies. This is especially true for Contract Research Organizations (CROs), which exhibit a stronger dependence on the supply chain. Unlike conventional pharmaceuticals, nuclear medicines are constrained by the half-lives of their radionuclides. This necessitates batch-by-batch production and staggered supply, making advanced stockpiling impractical. Consequently, precise coordination is required between upstream batch production and downstream clinical or research usage, mandating that nuclear medicine CXO companies secure stable sources of radionuclides and ensure reliable drug product supply.
For nuclear medicine CXO companies managing a high volume of projects with substantial radionuclide demand, this integrated operational scale not only provides more favorable pricing for isotopes but also significantly reduces logistics costs, demonstrating pronounced economies of scale.
The second major advantage of the one-stop nuclear medicine CRDMO model stems from improved efficiency. For CXO companies with full-chain capabilities, the transfer between different stages is highly convenient. For instance, on-site transfers between different segments are more efficient than the division of labor and collaboration across different companies or even regions.
Moreover, involving multiple collaborators can sometimes lead to ambiguity of responsibility and potential buck-passing due to excessive process segmentation, which can significantly compromise service quality. C Ray Therapeutics ensures efficiency enhancement through its full-chain coordination capabilities and the stable product supply provided by its fully automated production lines.
Additionally, according to Qiao Haitao, C Ray Therapeutics has designed unique logistics packaging for nuclear medicine products. The innovative packaging design meets the basic requirements of nuclear medicines while also complying with cold-chain standards, thus satisfying the transportation needs of radionuclide products requiring low-temperature storage. Leveraging Sichuan Airlines' convenient logistics channels, C Ray Therapeutics' radionuclide products can reach major medical institutions across China (except Xinjiang and Tibet) within 40 hours, achieving stable supply to economically developed regions such as East China, South China, and North China.
The third advantage of the one-stop CRDMO model comes from enhanced service value. It is well known that the later the development stage, the greater the product demand and the higher the project value. The one-stop service model can better ensure order continuity. It is understood that among C Ray Therapeutics' over 60 projects, more than five involve concurrent clinical sample supply, fully demonstrating its comprehensive service capabilities.
In October 2025, the Lutetium [¹⁷⁷Lu]-BL-ARC001 Injection, the first RDC drug candidate supported by C Ray Therapeutics' pilot-scale radiopharmaceutical services platform for Baili Pharmaceutical, received implicit approval for its clinical trial application. From the perspective of Baili Pharmaceutical's relevant responsible personnel, the rapid advancement of this innovative drug's development is inseparable from the strong support of its core CRDMO partner, C Ray Therapeutics.
C Ray Therapeutics' high-quality production capability is the foundation for achieving this. The company consistently maintains a 100% first-pass qualification rate in its critical batch productions.
The unique barriers within the nuclear medicine CXO sector will establish a first-mover advantage for early industry entrants. Currently, the nuclear medicine field is still in its early developmental stage, making the project experience of nuclear medicine CXO companies particularly valuable.
The entire process, from the release of radionuclides to the production and distribution of radiopharmaceuticals, requires seamless coordination to meet downstream R&D and therapeutic needs. Achieving this depends on tight integration across the full supply chain, along with high-standard and stable production capabilities, which in turn demand industry resource advantages and extensive project experience from nuclear medicine CXO enterprises.
Therefore, for companies already established in the nuclear medicine field, first-mover advantage can facilitate better collaboration with radiopharmaceutical companies and further accumulate industrial momentum. Recently, Novartis entered into a cooperation agreement with HTA, a subsidiary of China Isotope & Radiation Corporation (CIRC), to provide medical institutions and patients with supply and solutions for Pluvicto®.
As the nuclear medicine industry continues to evolve, industrial clustering and first-mover advantages will become increasingly pronounced in the nuclear medicine CXO domain. For enterprises considering entry into this field, engaging through equity investment or partnerships may represent a more efficient approach to entering the nuclear medicine CXO sector.
