The peptide paradigm shift: how Xiushi Biopharma is redrawing the map of the peptide industry
The expanding therapeutic application of peptide drugs, led by GLP-1-based therapies, across chronic disease areas—including diabetes, weight management, chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular conditions, and osteoarthritis—is driving rapid market growth. According to Frost & Sullivan, the global peptide drug market is projected to increase from $62.8 billion in 2020 to $141.9 billion by 2030. In addition, the period from 2014 to 2026 marks a peak in patent expirations for several major peptide drugs, which is expected to spur the entry of multiple generic products and further accelerate R&D efforts toward next-generation peptide therapeutics. As both novel and established molecules vie for market position, process optimization and scalable, compliant manufacturing are becoming key focus areas along the value chain, creating new opportunities for upstream players with expertise in intermediate and active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) development and production.
Despite the promising market outlook, few companies are equipped to rapidly engage in peptide drug R&D and large-scale manufacturing. A major reason lies in the inherent challenges of peptide-based drug development. For one, early-stage screening of peptide candidates involves substantial workload and high complexity: a peptide composed of 14 amino acids, for example, can theoretically form 10¹⁸ possible compound variants. Introducing non-natural amino acids further increases the combinatorial complexity by several orders of magnitude. For another, the field still lacks well-established discovery pathways and reliable target design methodologies. Although global peptide molecular libraries have achieved considerable size and diversity, they often fall short of meeting the practical demands of innovative drug screening. This is particularly true for long-chain peptides, where constructing physical compound libraries is extremely difficult, hampering targeted screening efforts.
The convergence and advancement of AI algorithms are now addressing these early-stage discovery and design bottlenecks. By learning biomolecular characteristics and simulating protein structure-function relationships, AI can transcend the limits of conventional approaches to design peptides with novel structures and biological functions. It can even generate preliminary structural models for complex long-chain and cyclic peptides—ushering in a transformative shift in peptide drug discovery.
However, identifying a novel peptide molecule is only the first step. The real challenge lies in crossing the "valley of death" between discovery and scalable synthesis. Technological innovations and AI-driven design have accelerated the identification of peptides with complex structures, which in turn introduces new manufacturing hurdles—such as difficult condensation reactions and elevated levels of process-related impurities—where conventional chemical synthesis methods often prove inadequate. Moreover, traditional peptide manufacturing processes typically max out at batch sizes of 2,000-3,000 liters, a scale insufficient to meet future ton-scale demand for peptide APIs.
Clearly, scaling peptide drug production presents multiple challenges. As chemical synthesis capacity gradually expands, those who can overcome the technical barriers associated with developing and manufacturing structurally complex peptides will be positioned to lead the next wave of growth in this evolving market. The peptide field has now entered an era where success will be determined by core technological capabilities.
The Competition between the Innovation and Scalability of Peptide Synthesis Technology
Current peptide synthesis methods are predominantly based on chemical approaches. With the rapid expansion of the GLP-1 drug market, the industry has begun optimizing production processes, showing a trend toward integrated development of both chemical and biosynthetic methods. Industry experts note that "biosynthesis offers advantages such as lower production costs, strong directional expression capabilities, and large-scale production capacity, representing the future development direction—this is a consensus within the peptide synthesis field."
The limitations of chemical synthesis underlie this shift. Producing peptide drugs via chemical synthesis involves numerous production steps and extended cycle times, while also generating substantial organic wastewater. The high costs and stringent requirements for hazardous waste treatment contribute to elevated production expenses and costly final products. Furthermore, chemical synthesis processes struggle with producing long-chain and complex peptides. More importantly, as chemical peptide synthesis technology matures and the supply of basic production equipment for peptide drugs has become more adequate in recent years, the number of Chinese enterprises with chemical peptide production capacity has increased, leading to noticeable homogenized competition within the industry. This is particularly evident for established products whose patents expired years ago, where numerous active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) suppliers have intensified competition in both the API and formulation markets. Consequently, competition among chemical peptide synthesis firms is essentially a comprehensive contest of production scale, cost advantages, and market strategy, with little relation to technological breakthroughs. Clearly, the mature and highly competitive chemical synthesis pathway no longer possesses the potential to unlock greater market value for peptides.
Traditional biosynthesis technologies also face multiple industry challenges. Their synthesis strategies are constrained by limited underlying technical approaches, being applicable only to a few types of peptides and exhibiting very low expression yields. This results in high capital investment and overall production costs, preventing effective substitution for chemical synthesis. Key reasons include: the low proportion of the target peptide chain in traditional fusion protein designs, hindering efficient mass production; and the lack of universal techniques suitable for diverse amino acid compositions, molecular cyclization, and modifications. Additionally, traditional biosynthesis faces high technical barriers and significant R&D difficulties in addressing engineering challenges such as large-scale, low-cost peptide preparation, cell factory construction, and downstream process development.
In the post-GLP-1 era, the number of complex-structured peptides is growing exponentially, yet traditional synthesis technologies are clearly unable to meet the production needs for all peptide categories. Moreover, demand for GLP-1 and next-generation GLP-1 products is expected to rapidly scale up in the coming years, with downstream demand for peptide drugs gradually evolving to ton-level quantities. However, production processes for many peptide APIs remain immature at this stage, with numerous steps requiring further exploration and validation. Coupled with long lead times for building peptide drug production capacity and the wide variety of final products, peptide synthesis and scale-up continue to face significant challenges.
How can the industry overcome the synthesis challenges of complex peptides and achieve successful commercialization? Some companies are attempting to address these industry problems using synthetic biology methods, aiming to capture the next growth opportunity in peptide drugs. However, synthetic biology in China started relatively late, creating a gap with other countries, and its application in the peptide field is even rarer. Recognizing the scarcity, high technical barriers, and strong clinical demand for peptide biosynthesis, the founders of Xiushi Biopharma—drawing on over ten years of experience in synthetic biology—established the company in 2020 to pioneer this field.
While the industry is still discussing "how to enter the peptide biosynthesis field," Xiushi Biopharma had already anticipated its development needs. Having focused on this industry for five years, the company has become one of China's first enterprises to achieve large-scale biosynthesis of complex short-peptide drugs. It not only possesses proprietary innovative biosynthesis technologies but has also established an efficient process development platform and team integrating AI technology, genetic engineering, enzyme engineering, fermentation engineering, protein engineering, and chemical engineering. This enables significant reduction in biosynthetic process R&D timelines and achieves efficient, low-cost, and scalable peptide biosynthesis with highly aligned biological design and pharmaceutical process requirements.
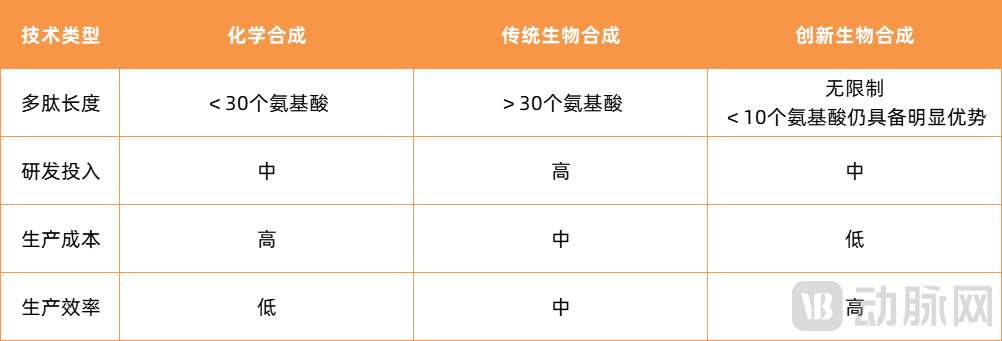 Comparative Analysis of Peptide Drug Production Technologies
Comparative Analysis of Peptide Drug Production Technologies
To date, Xiushi Biopharma's proprietary innovative biosynthetic platform has been applied in over ten peptide products. Leveraging core technology platforms including diverse protein building blocks and genetic element libraries, peptide chain structural modifications, and incorporation of non-natural amino acids, the company has successfully overcome challenges in the biosynthesis of short peptides and complex cyclic peptides. Furthermore, by integrating biological and chemical modification technologies, it has addressed a series of difficulties in manufacturing biosynthetic peptides, including cyclization involving multiple disulfide bonds, non-natural amino acid modifications, and fatty acid side chain modifications. It is noteworthy that peptides produced using this innovative biosynthetic process can achieve costs as low as 10–20% of those associated with chemical synthesis. Compared with traditional biosynthesis techniques, the production efficiency is improved more than fivefold while requiring smaller fermentation scale.
Simultaneously, Xiushi Biopharma continues to refine its technology platforms, utilizing AI for rapid process iteration. By drawing on its extensive collection of protein building blocks and enzyme libraries, the company has established neural network models aimed at shortening R&D cycles and enhancing biosynthetic performance. This approach not only accelerates process development timelines and elevates the standard of biological process delivery but also creates more cost-effective and qualitatively superior process solutions for the growing pipeline of innovative peptide drugs—particularly multi-target drug molecules—thereby increasing the efficiency and cost competitiveness of novel peptide drug development.
As the peptide industry enters an era defined by simultaneous technological iteration, surging demand, and production capacity restructuring, companies must continuously strengthen their internal capabilities to meet the evolving needs of peptide pharmaceutical clients. Through years of development, leading enterprises in peptide biosynthesis like Xiushi Biopharma have successfully built a formidable technological moat within the industry.
"Capacity + Ecosystem" Synergy
A breakthrough in synthesis technology is merely the entry ticket to the top tier of the peptide synthesis field. The crucial step that truly impresses industry chain partners and ensures long-term competitiveness in this sector is the efficient scaling and industrialization of that technology. Through five years of development, Xiushi Biopharma has established a fully integrated, end-to-end pipeline—spanning from laboratory R&D to scaled manufacturing, and finally to GMP-compliant drug production.
Currently, Xiushi Biopharma has built over 5,000 m² of AI-enabled R&D facilities and a 13,000 m² intelligent peptide drug production base. This infrastructure supports flexible manufacturing—from gram-scale R&D samples to ton-scale commercial products—capable of meeting diverse needs ranging from small-batch clinical trial materials to large-scale commercial supply. Leveraging this industrial capacity, Xiushi has successfully served clients across multiple fields, including therapeutic peptides, cosmetic peptides, and recombinant proteins. Notably, the company's newly operational intelligent peptide drug production base represents China's first GMP-compliant, large-scale production line specifically designed for peptide biosynthesis products, with synthetic biology at its core.

Xiushi Biopharma Commissions Intelligent Peptide Drug Production Base
It is evident that Xiushi Biopharma is redrawing the map of the peptide industry ecosystem by centering its strategy on innovative biosynthetic technology and intelligent manufacturing, providing one-stop empowerment for its industry chain partners. Through technological enablement, Xiushi has already assisted clients in fields such as AI-driven drug discovery and cell therapy—who demand high technical standards and quality in peptide synthesis—to complete the R&D and industrialization of complex structured peptides, collectively driving the formation of the industry ecosystem and enhancing its overall value.
Wu Yinsong, Founder and Chairman of Xiushi Biopharma, emphasized, "A client's successful commercialization means not only that the peptide molecule itself has been scaled up, but also that future cost accessibility is achieved. While helping partners overcome technical and scaling challenges, Xiushi Biopharma leverages project experience and market insights to deliver products that surpass industry benchmarks in cost, speed, and quality."
When discussing project collaborations, Yin Haixing, Co-founder and General Manager, noted, "Many clients, after engaging with Xiushi Biopharma, describe the experience as 'opening new horizons,' offering peptide molecular options they had never previously considered." This shift in perspective stems from the fact that before Xiushi's entry, the industry widely believed that complex peptides could not be commercialized and that biosynthetic technology could not be applied at scale in peptide production. However, Xiushi has demonstrated, through numerous real-world case data, that biosynthetic technology can indeed be used for commercializing complex peptides—with lower costs and higher efficiency. Yin stressed, "We should not dismiss feasibility based on the limitations of existing technology. Solving industry pain points is only a matter of time and technological breakthrough."
Xiushi Biopharma's technology and production lines have gained recognition not only within the industry but also from the capital markets. On November 21, the company announced the completion of a nearly 100 million Series A financing round, supported by new and existing investors including Huatai Zijin, Cuishi Capital, Jinding Capital, and Arshine Group. Prior to this, Xiushi had completed several earlier rounds with participation from institutions such as Chuangjing Capital and Jolmo Capital. The involvement of these firms fully reflects the capital market's high recognition and trust in Xiushi Biopharma as a leading enterprise in the peptide industry.
Endorsement from both industry partners and investors has accelerated Xiushi's development. The company is now accelerating its global deployment. In peptide API R&D, it is actively advancing regulatory submissions in multiple countries outside China. In large-scale peptide manufacturing, 80% of its customer orders originate from international markets, and its intelligent peptide drug production base is currently undergoing audits by overseas clients.

Exterior View of Xiushi Biopharma Synthesis Workshop
Why has Xiushi Biopharma, a startup founded just five years ago, been able to expand so rapidly in international markets—known for their higher standards for product quality and technology? Wu Yinsong explained to VCBeat, "The key to Xiushi's rapid growth lies in our consistent commitment to technological innovation and ecosystem development. To be candid, we often don't position ourselves purely as a 'service provider' (Party B), but rather join our clients as collaborative 'partners' (Party A) to jointly tackle industrial challenges in peptide synthesis. This is because peptide synthesis is an industry with high customer stickiness and significant barriers. Only by maintaining an open approach and actively collaborating with industry chain partners can we contribute the essential 'know-how'—understood only by practitioners—to the construction and refinement of the peptide industry ecosystem."
Moving forward, as the value proposition in the peptide industry shifts from pure production capacity toward technological innovation and ecosystem development, Xiushi Biopharma will—following the expansion of its intelligent production lines—deepen its collaboration with global pharmaceutical companies. The company aims to provide key insights for breaking through technical bottlenecks in the peptide sector and for strengthening industry-academia-research-application synergies, thereby injecting momentum into the high-quality development of the global peptide industry. It is anticipated that leading Chinese enterprises in peptide biosynthesis, represented by Xiushi Biopharma, will use innovative technology as a lever to drive systematic improvements across the entire industry chain in cost, speed, and compliance efficiency, unlocking sustainable, scalable, and well-regulated new value for their partners.
