The billion-dollar bispecific antibody era is here: who leads the next wave?
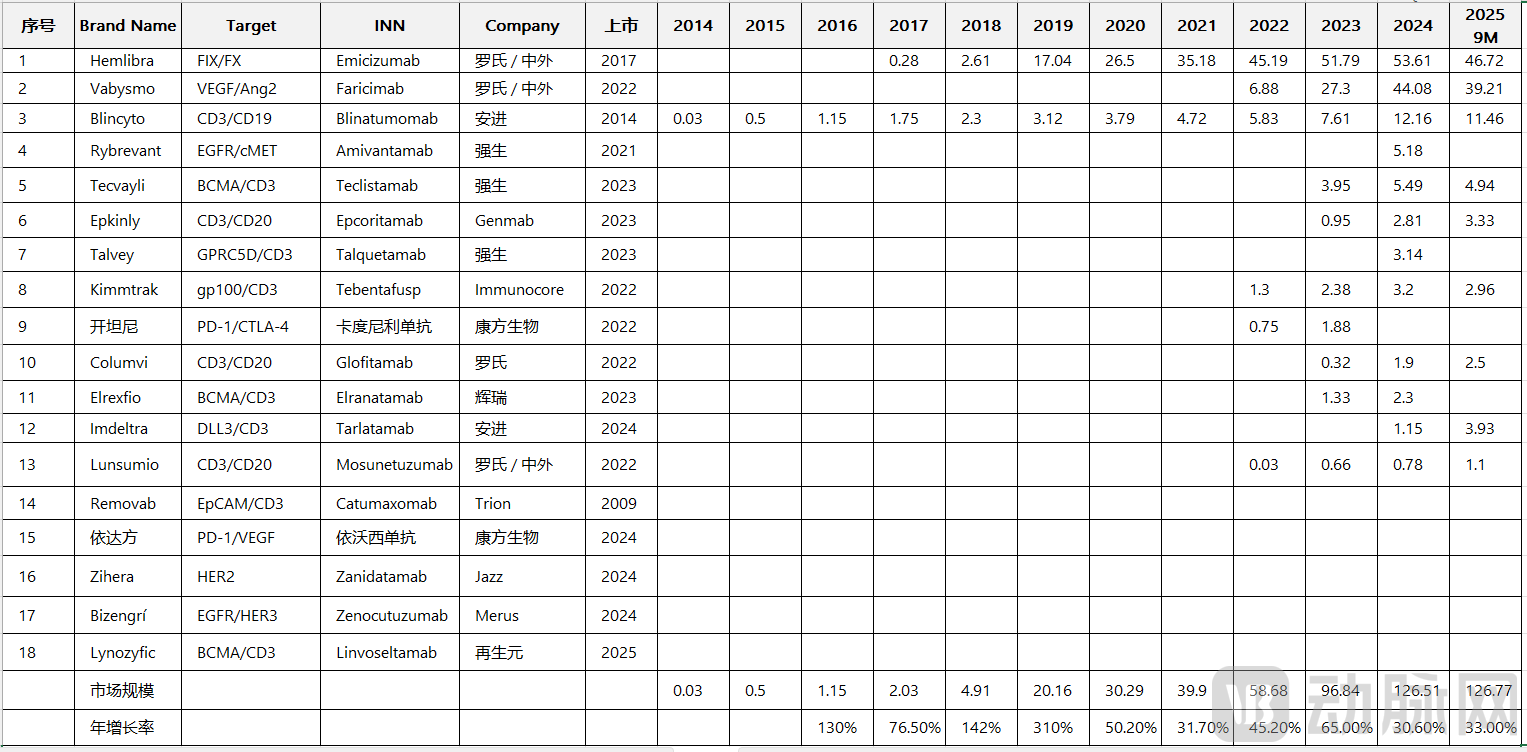
In the first three quarters of 2025, the global market for bispecific antibodies had reached $13 billion in revenue, a 33% year-on-year increase, with full-year revenue projected to surpass $17 billion. These figures signal that bispecific antibodies have matured from a technical concept into a commercial cornerstone and are rapidly securing their role as a key therapeutic modality in major disease areas such as oncology, autoimmune disorders, and ophthalmology.
While multinational pharmaceutical companies like Roche, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson currently lead the market, Akeso Biopharma is reshaping the global competitive landscape with its innovative immune-oncology bispecific antibody structure. This growth is propelled by the maturation of bispecific technology platforms, their demonstrated clinical value, and an urgent market need for next-generation treatments.
Annual Sales of Approved Bispecific Antibody Drugs
The Billion-Dollar Era for Bispecifics Antibody Has Arrived:
What's Driving the Boom?
In 2025, the global market for bispecific antibodies underwent a transformative leap, with annual revenue projected to surpass $17 billion. This milestone signals the arrival of the "billion-dollar bispecific antibody era."
Historically, monoclonal antibodies ushered in a therapeutic revolution due to their high specificity and targeting precision, establishing themselves as first-line treatments for numerous diseases. However, advancing research has revealed that monoclonal antibodies, which are limited to a single target, exhibit inherent limitations in treating complex disease pathways. The emergence of bispecific antibodies was designed precisely to overcome these constraints.
The core advantage of bispecific antibodies lies in their unique mechanism of action. By simultaneously engaging two distinct disease targets, they produce a synergistically enhanced therapeutic effect. Compared to monoclonal antibodies, which are restricted to a single target, bispecific antibodies achieve a more potent treatment response through dual targeting.
In the field of hemophilia treatment, Roche's Hemlibra stands as a prime example. Conventional hemophilia management primarily relies on regular infusion of clotting factors, an approach burdened by multiple inconveniences and persistent bleeding risks. As a bispecific antibody therapy, Hemlibra simultaneously targets both FIX and FX, effectively mimicking the function of coagulation factor VIII. This mechanism not only significantly reduces bleeding episodes but also markedly improves patients' quality of life. Since its market approval in 2017, Hemlibra has demonstrated remarkable commercial performance, with sales reaching $4.672 billion in the first three quarters of 2025 and a full-year projection exceeding $6 billion, capturing nearly half of the hemophilia treatment market.
In ophthalmology, bispecific antibodies have also demonstrated strong competitiveness. While traditional anti-VEGF monoclonal antibodies effectively inhibit angiogenesis in treating ocular conditions like wet age-related macular degeneration (wAMD), some patients gradually develop resistance over time, leading to diminished therapeutic response. Roche's VEGF/Ang2 bispecific antibody, Vabysmo, addresses this challenge by simultaneously targeting VEGF and Ang2, enabling more comprehensive suppression of both angiogenesis and inflammatory pathways, thereby enhancing treatment efficacy. With sales of $3.921 billion in the first three quarters of 2025 and an expected annual total surpassing $5 billion, Vabysmo has become the top-selling novel anti-angiogenic ophthalmic medication.
In cancer immunotherapy, bispecific antibodies have ushered in the "Immunotherapy 2.0" era. Taking PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibodies as an example—both PD-1 and CTLA-4 are critical immune checkpoints that tumor cells often exploit to evade immune surveillance. By concurrently blocking both checkpoints, PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibodies potently activate the immune system and enhance antitumor cytotoxicity. This bispecific design not only improves therapeutic outcomes but also mitigates the overlapping toxicities commonly observed with combination therapy using two separate monoclonal antibodies, offering cancer patients a more favorable treatment option.
Global Giants' Rivalry: The Competition of Roche, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson
Roche, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson have established themselves as undisputed leaders in the bispecific antibody field, leveraging their profound R&D expertise, extensive clinical experience, and robust commercialization capabilities. The competition among these pharmaceutical giants remains exceptionally intense.
Roche has taken a commanding lead in the bispecific arena, capturing nearly half of the global bispecific market with two blockbuster products: Hemlibra and the ophthalmic bispecific Vabysmo.
Roche demonstrates exceptional insight in target selection. Hemlibra addresses two critical targets in hemophilia treatment—FIX and FX—through an ingenious design that mimics the function of coagulation factor VIII, offering a revolutionary therapeutic option for hemophilia patients. Vabysmo, on the other hand, targets both VEGF and Ang2 signaling pathways in ophthalmology, effectively overcoming the resistance issues associated with traditional anti-VEGF monotherapy and improving treatment outcomes.
In clinical development, Roche fully utilizes its expertise in biomedicine to conduct large-scale, multicenter clinical trials, generating robust data to support product efficacy and safety. Commercially, Roche's extensive global distribution network enables rapid market penetration worldwide, broadening patient access. Hemlibra, for instance, has seen steadily increasing sales since its launch, not only delivering substantial revenue for Roche but also solidifying its leading position in the bispecific landscape.
Amgen has also demonstrated strong performance in bispecifics, maintaining competitive strength through strategic developments in both hematologic and solid tumors.
Its CD3/CD19 bispecific blinatumomab (Blincyto) has achieved remarkable success in hematologic malignancies. By targeting CD19 and CD3, it redirects immune cells to tumor cells, enhancing immune response and antitumor efficacy. Since its initial approval in 2014, Blincyto has shown steady sales growth, reaching $1.146 billion in the first three quarters of 2025, with full-year revenue projected to exceed $1.5 billion.
In solid tumors, Amgen's DLL3/CD3 bispecific tarlatamab has shown significant potential. In April 2025, Amgen released study results demonstrating that tarlatamab significantly improved overall survival in patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in clinical trials. This breakthrough offers new hope for many lung cancer patients and secures Amgen a foothold in the solid tumor bispecific market. Amgen continues to innovate in clinical development, actively exploring new indications and combination regimens to expand treatment options. On the commercial front, Amgen's strong reputation and broad market reach in biopharmaceuticals ensure successful product launch and adoption.
Johnson & Johnson has rapidly emerged in the solid tumor space with its EGFR/c-MET bispecific amivantamab (Rybrevant). As the world's first EGFR/c-MET bispecific antibody, Rybrevant received accelerated FDA approval in 2021 for the treatment of patients with advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations, following platinum-based chemotherapy. By simultaneously inhibiting both EGFR and c-MET signaling pathways, Rybrevant has demonstrated promising antitumor activity. In 2025, Rybrevant is in a phase of rapid commercial expansion, with full-year sales expected to surpass $700 million.
Additionally, Johnson & Johnson has built a presence in hematologic malignancies, with two hematology-focused bispecific antibodies projected to collectively generate over $1 billion in annual sales. In clinical development, Johnson & Johnson emphasizes both therapeutic efficacy and safety, implementing rigorous trial designs and data analysis to ensure product quality. Commercially, the company leverages its powerful brand influence and global marketing network to accelerate market entry and enhance product penetration.
Global Breakthrough of China's Strength
Amid the intense global competition in bispecific antibodies, several Chinese biopharmaceutical companies have begun to make their mark on the international stage, emerging as emblematic representatives of China's original innovation in the bispecific field.
Akeso Biopharma has independently developed two globally first-in-class bispecific antibodies—cadonilimab (PD-1/CTLA-4, trade name: Candonil) and ivonescimab (PD-1/VEGF, trade name: Yifang). Both molecules offer unique advantages. Cadonilimab simultaneously targets two "Nobel-recognized" immune checkpoints, PD-1 and CTLA-4. Through synergistic action, it more effectively activates the immune system and enhances tumor-killing capacity. This novel antitumor mechanism underpins cadonilimab's superior efficacy, with significantly reduced toxicity and improved safety compared to traditional combination therapies, leading to better patient tolerability.
Ivonescimab targets two "blockbuster-level" pathways—PD-1 and VEGF—enabling dual mechanisms of action: immune activation and anti-angiogenesis. On the immune front, it blocks the PD-1 checkpoint, activating T cells and strengthening immune recognition and attack of tumor cells. In parallel, it inhibits VEGF-mediated angiogenesis, cutting off tumor nutrient supply and metastatic routes, thereby suppressing tumor growth and spread. This innovative dual-target design has demonstrated potent activity across multiple tumor types.
Clinical data remain the ultimate test of a drug's efficacy, and both of Akeso's bispecific candidates have delivered impressive results in trials. In the Phase III HARMONi-2 study, ivonescimab monotherapy was compared head-to-head with the blockbuster pembrolizumab as first-line treatment in PD-L1-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and achieved statistically significant positive outcomes. The median progression-free survival (mPFS) with ivonescimab was 11.14 months, nearly doubling the 5.82 months observed in the control arm, and reduced the risk of disease progression or death by 49%. These results establish ivonescimab as the first drug globally to outperform the incumbent "blockbuster" in a Phase III head-to-head trial, highlighting the considerable potential of China-developed bispecifics in oncology.
Cadonilimab has also demonstrated outstanding efficacy in a clinical trial for recurrent/metastatic cervical cancer. In the overall population, cadonilimab treatment resulted in a median overall survival (mOS) exceeding 18 months (not reached), an objective response rate (ORR) of 31.3%, and a complete response (CR) rate of 13.1%. Among PD-L1-positive patients, the ORR reached 43.8%, median PFS was 6.34 months, and median OS was not reached. These data confirm that cadonilimab not only extends patient survival but also improves response rates, offering new hope for women with cervical cancer.
Market performance is a key indicator of a drug's value. Although specific sales figures for the two bispecifics have not been disclosed, both have entered a "rapid uptake phase." In the first half of 2025, Akeso reported commercial revenue of RMB 1.402 billion, a year-on-year increase of 49.20%, largely driven by volume growth following the inclusion of both cadonilimab and ivonescimab in China's National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) starting January 2025. This robust performance underscores strong market acceptance and substantial commercial potential for Akeso's bispecific portfolio.
Akeso's success stems not only from the exceptional performance of its products but also from its innovative approach of shifting immunotherapy from "single-target inhibition" to "multi-pathway synergy," positioning its candidates as potential foundational therapies in the post-PD-1 era. This pioneering concept has opened new avenues for cancer treatment and attracted attention from multiple multinational pharmaceutical companies, several of which have begun developing assets with similar mechanisms. This trend signals that China's innovators are no longer just following but are now running alongside and even beginning to set the pace in global R&D, with Akeso increasingly recognized as a leader in the global bispecific antibody landscape.
As a leading traditional pharmaceutical company in China, Hengrui Pharma has demonstrated its profound R&D expertise and platform-based capabilities in the bispecific antibody field. Leveraging its self-developed PROTAC and common light chain technology platforms, the company has built a robust bispecific pipeline. Its core product, the PD-L1/TGF-β bispecific antibody SHR-1701, has emerged as the frontrunner in China for this target. It has shown promising efficacy and safety in clinical studies across multiple cancer types, including cervical cancer and biliary tract cancer, and has now entered the regulatory submission phase.
Additionally, several other candidates, such as the CD3/BCMA bispecific HRS-9531 and the PD-L1/HER2 bispecific antibody, have progressed to pivotal clinical stages. Backed by its strong clinical development and commercial capabilities, Hengrui aims to replicate its prior success in monoclonal antibodies and small molecules within the bispecific arena, indicating considerable potential for future growth.
Leveraging its established antibody development platform, Innovent Bio has adopted a differentiated strategy in the bispecific antibodies space. Its core pipeline includes IBI323, a LAG-3/PD-L1 bispecific antibody with one of the most advanced global development progress in this class. It is designed to address patients who have developed resistance to PD-1 inhibitors.
Meanwhile, the VEGF/Ang2 bispecific antibody (a Faricimab biosimilar candidate), developed in collaboration with Roche, is also advancing rapidly in China, positioning Innovent Bio to capture a share of the substantial ophthalmic market. Innovent Bio's strategy focuses on identifying novel combinations of validated targets and exploring combination therapies between its bispecific candidates and other internal product lines. This approach aims to build a synergistic treatment ecosystem. Supported by solid clinical execution capabilities and an established commercial network, Innovent Bio has laid a strong foundation for the future launch of its bispecific antibody products.
BioKin Pharma has distinguished itself through its unique "BsAb-ADC" platform, establishing a pioneering position in this global field. Its lead asset, the EGFR/HER3 bispecific antibody-drug conjugate BL-B01D1, represents the full capabilities of this technology platform. The bispecific antibody component simultaneously binds to both EGFR and HER3, enabling dual inhibition of tumor signaling pathways and enhancing tumor-specific drug accumulation. This is followed by precise cell killing mediated by the small-molecule toxin payload. BL-B01D1 has demonstrated impressive efficacy in multiple solid tumors, including advanced non-small cell lung cancer and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Certain clinical data are comparable or even superior to those of established ADC therapies. The program has already secured international licensing agreements totaling several hundred million US dollars and has entered global pivotal clinical trials, positioning BL-B01D1 as a highly promising "Innovated in China" product in the international BsAb-ADC landscape.
EpimAb Biotherapeutics' core competitiveness lies in its proprietary FIT-Ig® (Fabs-In-Tandem Immunoglobulin) bispecific antibody technology platform. This platform effectively addresses common challenges in bispecific development such as chain mispairing and stability issues, enabling efficient generation of bispecific molecules with native IgG structure. Leveraging this leading platform, EpimAb is not only advancing its own core pipeline assets—including the CD3×BCMA bispecific EMB-06 (for multiple myeloma) and the PD-1×LAG-3 bispecific EMB-02—but has also established partnerships through technology licensing with multiple domestic and international pharmaceutical companies (such as KYM and Chia Tai Tianqing). This strategy represents a business model innovation transitioning from "product development" to "technology out-licensing," offering another successful paradigm for the globalization of China's bispecific antibody technology.
3SBio has rapidly emerged as a key contender in the global bispecific antibody arena through a landmark licensing agreement. On May 20, 2025, the company entered into a partnership with Pfizer for the overseas rights to its PD-1/VEGF bispecific antibody SSGJ-707, in a deal valued at up to $6.05 billion. The transaction included a groundbreaking $1.25 billion upfront payment—setting a new record for out-licensing of innovative drugs from China—and triggered a more than 70% surge in the stock prices of 3SBio-affiliated entities over three consecutive trading sessions.
SSGJ-707, a cornerstone asset in 3SBio's pipeline, employs a differentiated molecular design that enables dual blockade of PD-1 and VEGF pathways. Early-stage clinical studies have shown superior potential across multiple indications, including non-small cell lung cancer. Its unique structural optimization presents new opportunities for optimizing the efficacy-safety profile. The landmark deal prompted immediate market reactions. Shares of Akeso Biopharma—previously the category leader—declined over 5% on the same day, reflecting a market reassessment of the competitive landscape in the PD-1/VEGF bispecific segment. 3SBio's assertive market entry signals a shift from single-player dominance to a dynamic two-leader competition.
Through this collaboration, 3SBio has not only secured substantial R&D funding and access to a premier global platform but has fundamentally reshaped the competitive dynamics of the global PD-1/VEGF bispecific field. This achievement demonstrates that Chinese pharmaceutical companies now possess the capability to drive innovation in core therapeutic areas on the global stage.
The Future is Here: What's the Next Stop for Bispecific Antibodies?
Looking ahead, bispecific antibodies continue to show promising development prospects, with their applications expanding from oncology to non-oncological areas, bringing hope to more patients.
Autoimmune diseases represent an important development direction for bispecific antibodies. These conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis, occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues and organs. These diseases significantly impact patients' quality of life, and current treatments have certain limitations. By simultaneously targeting two pathways involved in autoimmune responses, bispecific antibodies can more precisely regulate the immune system and suppress abnormal immune reactions, thereby offering new strategies for treating autoimmune diseases.
Currently, several T-cell engager (TCE) bispecific antibodies have entered clinical research stages, providing preliminary validation of their potential in autoimmune disease treatment. For example, the CD3/CD19 bispecific antibody CN201 has demonstrated favorable safety and efficacy in treating relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), with potential future applications in autoimmune diseases. A study published in Nature Medicine in April 2024 showed that the CD3/CD19 TCE blinatumomab successfully treated six patients with severe multidrug-resistant rheumatoid arthritis. Growing evidence suggests that TCE bispecific antibodies hold broad application prospects in autoimmune disease treatment and are expected to become important therapeutic approaches in this field.
In chronic disease areas such as neurological and metabolic disorders, bispecific antibodies also show promising potential. Taking Alzheimer's disease as an example, abnormal aggregation and deposition of β-amyloid (Aβ) is a core pathological mechanism in Alzheimer's development. While several Aβ-targeting monoclonal antibodies have been approved globally worldwide, limited blood-brain barrier penetration restricts their therapeutic efficacy and presents certain safety concerns.
Akeso Biopharma's AK152 is a bispecific antibody that simultaneously targets both Aβ and a blood-brain barrier (BBB) highly expressed receptor. On one hand, its Aβ-binding domain not only interacts with Aβ plaques but also highly selectively binds to more neurotoxic soluble Aβ oligomers. On the other hand, it significantly enhances AK152's brain penetration through receptor-mediated transcytosis utilizing the BBB highly expressed receptor. Preclinical results demonstrate that AK152 exhibits significant biological activity and favorable safety characteristics. Compared to monoclonal antibodies, it effectively improves brain antibody exposure, accelerates Aβ plaque clearance, and shows significantly superior therapeutic efficacy, potentially offering new hope for Alzheimer's disease patients.
In metabolic diseases, bispecific antibodies may become new options for treating conditions such as obesity and diabetes. By simultaneously targeting two metabolism-related pathways, bispecific antibodies can more effectively regulate metabolic processes and improve patient outcomes. Although current research remains in early stages, preliminary results have demonstrated certain potential worthy of further investigation.
In the coming years, with more clinical data readouts, exploration of combination therapies, and application of novel platform technologies, the bispecific antibody market will experience a second wave of rapid growth. The global bispecific antibody market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 44.4%, reaching $224.6 billion by 2032. During this process, bispecific antibodies will continue to innovate and optimize, providing more effective treatment options for patients and becoming an important pillar in the biopharmaceutical field.
Conclusion
The bispecific antibody market stands at the inflection point of a second wave of explosive growth. The journey from $13 billion to potentially exceeding $30 billion or even $50 billion will be driven not only by technological advancements but also by clinical value and commercial ecosystem development. While established leaders like Roche, Amgen, and Johnson & Johnson continue to set the pace, emerging forces such as Akeso Biopharma are demonstrating superior capabilities in structural innovation and clinical strategy.
In the coming decade, competitive dominance will belong to those who first achieve breakthroughs in non-oncological applications and define new standards in combination therapies.
