China's innovative drug market enters the post-BD era
The recent cooling of the innovative drug market, which had been thriving since the beginning of the year, is now becoming evident.
In terms of market performance, significant corrections have recently been observed in the innovative drug sector across both the Hong Kong and A-share markets. Based on our analysis of the constituent stocks of the Hong Kong Innovative Drug Index and A-share innovative pharmaceutical companies, most of these companies have seen declining stock prices since August 1st, with the steepest drop approaching 50%.
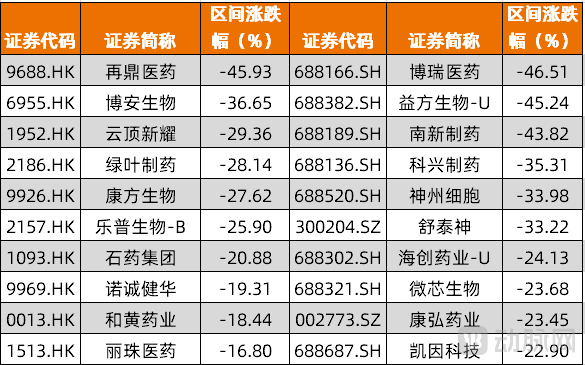
Figure 1. Hong Kong Innovative Drug Index Constituents and A-Share Innovative Drug Companies with Largest Declines (August 1, 2025 - November 18, 2025 | Source: Wind, VCBeat compilation)
The surge in BD (Business Development) deals was the primary driver behind this round of innovative drug market growth. However, as the growth rate of such transactions slows, merely pursuing the total deal value no longer meets investor expectations. Stakeholders are now reassessing whether these licensing agreements can deliver sustained value enhancement for companies. The innovative drug industry has entered a post-BD boom era.
BD activity shows signs of cooling across multiple fronts.
From a surface-level perspective, the first half of this year witnessed intense activity in innovative drug BD deals, with major transactions emerging frequently. On May 20, 3SBio's collaboration with Pfizer featured a groundbreaking $1.25 billion upfront payment—setting a new record for upfront payments in China's innovative drug sector—with the total deal value exceeding $6 billion. On June 13, CSPC Pharmaceutical out-licensed its AI platform to AstraZeneca for the development of novel oral small-molecule drug candidates, focusing on indications such as immune-related diseases, in a partnership with a potential total value of $5.33 billion. In addition, companies including Innovent, Harbour BioMed, and Hansoh Pharma have also announced significant BD agreements.
In July, Hengrui Pharma entered into a portfolio licensing agreement with GSK involving 12 products, with an upfront payment of $500 million and a potential total deal value of up to $12 billion, driving market sentiment around innovative drug BD to its peak. In the three months that followed, however, the fervor for such transactions began to subside.
According to data from PharmaCube, the total value of China-related licensing deals for innovative drugs in the first half of 2025 reached $60.8 billion, representing a 129% year-on-year increase. By comparison, the total deal value for the first three quarters of the year amounted to $93.7 billion, reflecting a lower growth rate of 64% year-on-year. This deceleration in growth indicates a noticeable cooling in China's innovative drug BD activity starting in the third quarter.
In the third quarter of 2025 alone, the total value of China-related licensing deals reached $32.9 billion, roughly comparable to approximately $30.6 billion during the same period last year, indicating that while deal values have sustained at a high level, growth momentum has indeed slowed.
Investor sentiment has reflected this shift, with both Innovent Bio's and Qyuns Therapeutics' BD deals in the second half of the year receiving a tepid market response.
On October 22, Innovent Bio entered into a collaboration with Takeda Pharmaceutical focused on next-generation immuno-oncology (IO) and ADC therapies. The partnership centers on two late-stage assets, IBI363 and IBI343, along with an early-stage candidate, IBI3001. The transaction includes an upfront payment of $1.2 billion, which comprises a $100 million strategic equity investment, with a total potential deal value of up to $11.4 billion.
Unlike most companies that opt to out-license molecules for short-term gains, Innovent Bio and Takeda Pharmaceutical have established a co-development and co-commercialization (Co-Co) model, sharing both risks and profits. Specifically, the two companies will co-develop IBI363 globally, sharing development costs on a 40/60 basis (Innovent/Takeda), while also co-commercializing the asset in the United States with profits or losses shared under the same 40/60 split.
This Co-Co model signals Innovent's longer-term ambition—not merely to mitigate R&D risk or secure near-term revenue, but to leverage collaboration with a multinational corporation (MNC) to expand its product overseas, capture commercial value in mature markets like the U.S. and Europe, and accumulate resources for future programs. Moreover, the 40% profit-sharing arrangement offers substantial long-term upside potential.
However, some investors expressed concerns over the model's requirement for sustained capital investment, with others viewing the approach as overly aggressive, leading to cautious market sentiment. On the day of the announcement, Innovent Bio's stock opened higher but closed down 1.96%, and has since traded sideways—reflecting significant investor divergence.
Just six days later, Qyuns Therapeutics entered into a global exclusive collaboration and licensing agreement with Roche for its bispecific candidate QX031N. The deal includes an upfront payment of $75 million, with potential milestone payments of up to $995 million. Although the upfront payment appears modest, the fact that QX031N is still in the preclinical stage meant the terms exceeded market expectations.
Following the announcement, Qyuns Therapeutics' stock exhibited a similar pattern of opening higher before closing down 8.23% on the first trading day, with subsequent declines reaching up to 25% cumulatively. The market remains skeptical about early-stage assets due to their prolonged development cycles and high risks, viewing such licensing deals as having limited potential to enhance companies' fundamental value.
These two recent representative cases clearly demonstrate a fundamental shift in how capital markets evaluate licensing transactions: the focus has transitioned from prioritizing upfront payments and total deal values to assessing long-term business fundamentals—specifically, whether a product can deliver sustainable value enhancement.
The innovative drug industry has now entered a post-BD boom era.
The innovative drug industry has now entered an era of global competition, with multiple paths available for product development and subsequent commercialization—companies can pursue independent development, out-license pipeline assets, or engage in collaborative partnerships. However, regardless of the chosen approach, product strength remains the decisive factor. This means the therapeutic must address unmet clinical needs and demonstrate potential to become a blockbuster drug with Best-in-Class (BIC) or First-in-Class (FIC) qualities.
Unlike other sectors that require comprehensive evaluation of multiple dimensions—including founding team, brand value, manufacturing capacity, and commercial infrastructure—in the innovative drug industry, the product itself reigns supreme.
1) DualityBio: DB-1311
DB-1311 is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting B7-H3. The molecule employs a humanized anti-B7-H3 IgG1 monoclonal antibody conjugated via a cleavable linker to P1021—a topoisomerase I inhibitor payload. Its overall design strategy aligns with Daiichi Sankyo's DS-7300.
DB-1311 achieves high selectivity by targeting the 4Ig B7-H3 isoform, predominantly expressed on tumor cells overexpressing B7-H3. It demonstrates over 1,000-fold higher binding affinity for this isoform compared to the 2Ig B7-H3 subtype typically found on normal cells. This selectivity enables precise delivery of the payload to tumor cells. Moreover, DB-1311 exhibits stronger tumor cell binding capacity than Daiichi Sankyo's DS-7300.
Designed with a drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR) of 6—higher than that of DS-7300—DB-1311 demonstrates enhanced antitumor activity, with its highest non-severe toxic dose (HNSTD) reaching 80 mg/kg.
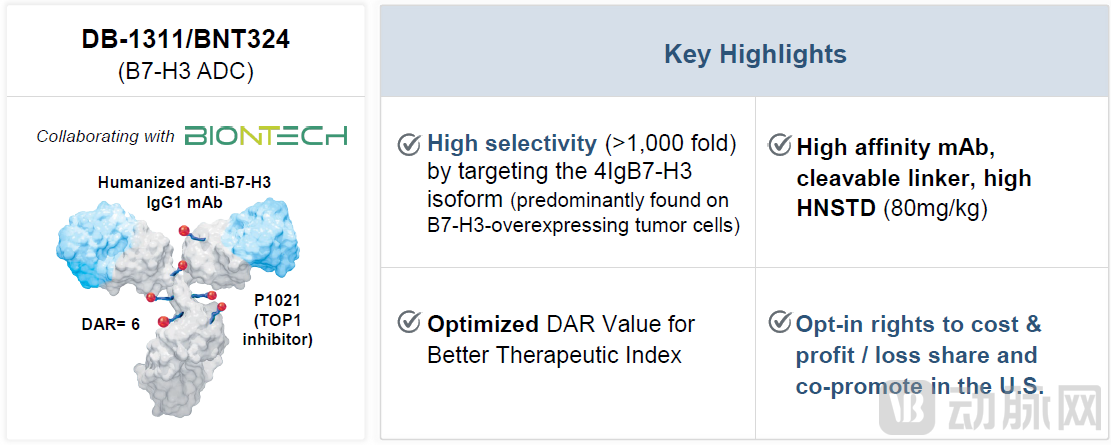
Figure 2. Core Features of DB-1311 (Source: DualityBio R&D Day)
DB-1311's latest clinical results were disclosed in an oral presentation at this year's American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting. The data showed objective response rate (ORR) of 42.3%, disease control rate (DCR) of 90.4%, and a 9-month rPFS rate of 58%. Additionally, no severe adverse events were observed with DB-1311.
Duality Biologics has achieved a strategic overtaking by expanding into the mCRPC indication. While Daiichi Sankyo's DS-7300 holds the global lead in clinical development for SCLC and is progressing faster than Duality's DB-1311 in this specific indication, Duality demonstrated strategic ingenuity by expanding into mCRPC beyond SCLC—enabling it to surpass competitors in clinical progress for this particular indication and establishing the most notable highlight for DB-1311.
Duality Biologics is currently advancing DB-1311 from a later-line to a first-line treatment for mCRPC, while simultaneously exploring other indications and combination therapies to continuously expand the product's commercial potential.
A partnership with BioNTech is accelerating the commercialization timeline. In April 2023, Duality Biologics entered into a collaboration agreement with BioNTech, granting global rights for the two ADC drug candidates DB-1311 and DB-1303 outside Greater China. Duality received an upfront payment of $ 170 million and is eligible for milestone payments exceeding $1.5 billion. Leveraging BioNTech's resource advantages will enable Duality to accelerate the product's path to market. More importantly, the experience gained from these projects can provide valuable reference for Duality's future independent global expansion efforts for subsequent products.
DB-1311 has the potential to become a blockbuster drug with peak sales exceeding $2 billion. Novartis' radiopharmaceutical Pluvicto, also used for mCRPC treatment, recently achieved blockbuster status. Pluvicto generated $1.392 billion in full-year 2024 revenue, representing 42% year-on-year growth, and reached $1.389 billion in sales during the first three quarters of 2025, growing 33% year-on-year with strong momentum. Based on Pluvicto's commercial performance, DB-1311 is projected to achieve $2-3 billion in overseas sales and peak sales of approximately 2 billion in China.
2) Laekna Therapeutics: LAE-102
LAE102 is an ActRIIA (Activin Receptor Type IIA) monoclonal antibody independently developed by Laekna Therapeutics, primarily for the treatment of obesity. It demonstrates dual effects of reducing fat and increasing muscle mass.
When combined with GLP-1 receptor agonists, LAE102 can further reduce adipose tissue while significantly counteracting muscle loss associated with GLP-1 agonist therapy, supporting healthier weight loss.
Eli Lilly supported clinical advancement. On November 20, 2024, Laekna Therapeutics announced a collaboration agreement with Eli Lilly, under which Lilly will conduct Phase I clinical trials for LAE102 in the United States and bear all associated costs. Laekna retains global rights to LAE102. The fact that Lilly is funding U.S. Phase I studies without securing rights to the asset underscores the compound's promising profile and suggests broader industry interest beyond Lilly alone. Laekna remains positioned to select future partners based on clinical progress.
Among ActRIIA/B receptor inhibitors, Eli Lilly's bimagrumab is a leading candidate. Phase IIb data presented at the 2025 ADA Scientific Sessions showed that monotherapy with bimagrumab led to a 10.8% weight reduction over 72 weeks, with 100% of the loss coming from fat mass and a 2.5% increase in lean mass. In combination with semaglutide, treatment resulted in an average weight reduction of 22.1% at 72 weeks, with 92.9% from fat loss and only 2.9% from muscle.
These clinical results for bimagrumab also highlight the potential commercial value of LAE102, which trails closely behind in clinical development.
LAE102 has demonstrated favorable efficacy and safety. On September 29, 2025, Laekna released multiple-ascending dose (MAD) data from its Phase I trial: in the 6 mg/kg cohort at week 5, lean mass increased by 1.7% and fat mass decreased by 2.2% from baseline. After adjusting for the placebo group, lean mass increased by 4.6% and fat mass decreased by 3.6%.
Moreover, LAE102 was well-tolerated with no serious adverse events reported. The trial did not observe side effects commonly associated with other drugs in this class, such as significant gastrointestinal reactions, muscle spasms, or acne. As a potential combination therapy with GLP-1 agents, LAE102 exhibits blockbuster potential.
3) CStone Pharmaceuticals: CS5001
CS5001 is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-like Orphan Receptor 1 (ROR1). It features a novel design incorporating a tumor-specifically activated pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) prodrug payload and linker. The mechanism involves CS5001 being internalized by tumor cells, where the linker is cleaved by specific enzymes highly expressed in tumor lysosomes to release the PBD prodrug. This prodrug is subsequently activated within tumor cells to exert cytotoxic effects. This "dual-control" mechanism—combining a specialized linker with a prodrug strategy—effectively mitigates toxicity issues commonly associated with traditional PBD payloads, resulting in a wider therapeutic window.
CS5001 is the first ROR1-targeting ADC to demonstrate clinical efficacy in both solid tumors and lymphomas, showing potential as a Best-in-Class (BIC) therapeutic.
At the 66th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting (ASH 2024), CStone Pharmaceuticals presented updated clinical data on CS5001 monotherapy in advanced lymphoma. From effective dose levels onward, CS5001 achieved an objective response rate (ORR) of 60.0% in advanced Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and 56.3% in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). At the preliminary recommended Phase II dose level (DL8, 125 μg/kg), the ORR reached 76.9% in patients with advanced B-cell lymphoma.
Earlier at the 2024 ASCO annual meeting, CStone disclosed that CS5001 demonstrated promising activity across multiple solid tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, and ovarian cancer.
Global multicenter trials of CS5001 are currently underway in the United States, Australia, and China. Patient enrollment is progressing steadily for cohorts with aggressive and indolent advanced lymphoma, with plans to potentially expand into a single-arm Phase II registrational study. Combination therapy studies with CS5001 are also advancing. The broad activity of CS5001 across both solid tumors and lymphomas positions it as a potential blockbuster drug with future peak sales exceeding $1 billion.
Since the second half of this year, particularly after August, the slowing growth rate of licensing deals has led to increasing market skepticism toward the innovative drug sector. The very transactions that fueled the market rally in the first half are now being met with divergent opinions, with bearish sentiments such as "selling unripe crops" and "one-wave flow" becoming increasingly frequent.
Setting aside BD activities, there is undeniable consensus that China's innovative drug sector has entered a growth cycle. Whether to engage in BD is merely a means, not an end—the ultimate goals remain addressing clinical needs as effectively as possible and translating these solutions into sustainable commercial value.
Although market enthusiasm for innovative drugs has cooled compared to July, with many stocks experiencing significant declines, several bright spots remain in the sector. BeOne Medicines (formerly BeiGene)'s third-quarter earnings substantially exceeded expectations, driving its share price back toward previous highs. Global sales of zanubrutinib surpassed $1 billion in Q3, representing 51% year-on-year growth and emerging as BeOne Medicines' standout performer. Meanwhile, the clinical progress of SSGJ-707, developed through the 3SBio-Pfizer collaboration, has exceeded expectations, driving the Shanghai-listed shares of 3S Guojian Pharmaceutical to record highs.
These developments collectively illustrate that in the post-BD boom era, the mere act of signing deals matters less than a product's development prospects and its ability to deliver lasting value to the company.
