From imports to innovation: mega-financing fuels the race for China's next-gen phaco-vitrectomy systems
On the map of China's medical device industry, there have always been certain long-standing "gaps"—not due to limited market size, but because the technological barriers were "too high to surmount."
Over the past decade, Chinese companies have successively made breakthroughs in several high-end ophthalmic devices, including surgical microscopes, fundus cameras, OCT systems, and intraocular lenses. However, one highly specialized segment remains overwhelmingly dominated by international giants such as Alcon, Bausch + Lomb, Zeiss, Johnson & Johnson, and BVI, which collectively hold over 90% of the market share. Among them, Alcon alone occupies nearly half of the entire market. To this day, no domestically manufactured device in this category has achieved regulatory approval in China.
Yet this seemingly "static" field has suddenly gained momentum this year:
In September 2025, Sierra Medical—developer of China's first dual-blade, dual-pneumatic vitreous cutter with a cutting speed of 20,000 CPM—secured over CNY 100 million in Series A funding, earmarked specifically for the deep development of its proprietary combined phaco-vitrectomy system.
Almost simultaneously, the AIER Healthcare Investment Group invested tens of millions of yuan in New Eyes Medical (Stock Code: 430140), focusing on the R&D and regulatory registration of the MTP5000 combined phaco-vitrectomy system.
In March, TowardPi Medical made industry headlines with a CNY 500 million E+ round of financing, with its product pipeline also targeting this very segment.
Earlier, at the beginning of the year, Brisight Nord—equipped with a dual-pneumatic vitreous cutter featuring a base cutting speed of 10,000 CPM—received Series A+ funding from Wuxi High-Tech Investment.
A quiet but determined race to the top is now underway in this once-dormant field, as Chinese companies vie to develop homegrown combined phaco-vitrectomy systems.
Why has the combined phaco-vitrectomy system captured the industry's undivided attention? The answer lies in understanding "phaco" and "vitrectomy" themselves.
In ophthalmic surgery, "phaco" (phacoemulsification) and "vitrectomy" represent two historically distinct domains. The former employs high-frequency ultrasound to emulsify and aspirate the clouded lens, serving as the core procedure in cataract surgery. The latter utilizes a vitrectomy machine to perform cutting, aspiration, and infusion inside the eyeball, addressing complex posterior segment conditions such as retinal detachment, macular holes, and diabetic retinopathy.
From a disease coverage perspective, phacoemulsification specializes in cataracts, while vitrectomy broadly encompasses vitreoretinal diseases (including retinal detachment, macular disorders, infectious endophthalmitis, etc.). Consequently, the phacoemulsification system and the vitrectomy machine have become two cornerstone devices in the ophthalmic operating room, supporting the anterior and posterior segment surgical systems respectively—each with entirely separate operational platforms and consumable ecosystems.
However, as clinical cases grow more complex and surgical philosophies converge, a rising number of patients present with concurrent cataract and vitreoretinal pathologies, or require multiple issues to be addressed in a single procedure. Frequently switching between consoles and re-establishing infusion systems not only prolongs surgical time but also increases the risks of infection and tissue trauma.
It is precisely against this backdrop that the combined phaco-vitrectomy system has emerged. By integrating multiple modules—including phacoemulsification, vitreous cutting, infusion, aspiration, and illumination—into a unified platform with intelligent control switching, this system enables a single device to simultaneously address both cataract and vitreoretinal procedures.
"The only treatment for cataracts and vitreoretinal diseases is phaco-vitrectomy surgery, and the only equipment capable of performing both procedures is the combined phaco-vitrectomy system," stated Zhang Chi, founder of Xiran Health. He emphasized that as patient conditions grow increasingly complex—particularly with the rising annual incidence of patients presenting with both cataracts and vitreoretinal pathologies—the limitations of relying solely on traditional standalone devices have become apparent, intensifying the clinical demand for integrated phaco-vitrectomy platforms.
For surgeons, these combined systems integrate phacoemulsification and vitrectomy capabilities, enabling seamless transition between anterior and posterior segment procedures without changing consoles. This creates a fluid, continuous workflow particularly advantageous for managing combined anterior-posterior segment pathologies. For patients, undergoing a combined procedure during a single hospital visit reduces the number of anesthesia events and overall surgical time, leading to better surgical outcomes and enhanced safety. For healthcare facilities, a single platform covering two core ophthalmic procedures improves operating room utilization, rapidly expands day-case and primary-level surgical capacity, and significantly increases both revenue per device and turnover rate—achieving a triple win of "minimally invasive care, operational efficiency, and financial sustainability."
However, precision instruments often come with inherent complexity.
"The phaco module is relatively mature—the real challenge lies in the vitrectomy system," Wang Yingqi, co-founder of TowardPi Medical, explained to VCBeat. The control unit of the vitrectomy system represents the core difficulty in product development and is critical to determining the device's performance and stability. Vitrectomy is typically classified as a Level 4 procedure—one of the highest complexity grades in ophthalmic surgery. The technical barriers for vitrectomy systems are substantial, encompassing challenges in gas-fluid control, Venturi/peristaltic pump management, vacuum stability, and feedback mechanisms. These systems integrate complex mechanical, electrical, and embedded components spanning multiple interdisciplinary fields, requiring prolonged debugging cycles and incurring significant R&D costs.
Zhang Chi, founder of Xiran Health, expressed a similar perspective, noting that the development of combined phaco-vitrectomy systems and their consumables spans multiple disciplines including mechanical and electrical engineering, acoustics, optics, pressure sensors, software algorithms, precision machining, and injection molding. Furthermore, these devices require highly integrated phacoemulsification, vitreous cutting, illumination, and infusion-aspiration systems that must operate with reliable synergy, placing extreme demands on integration capabilities and control precision. Critical technical challenges during design include the consolidation of fluidics control and energy systems, along with maintaining kinetic stability during micro-scale cutting procedures. Additionally, as Class III medical devices, combined phaco-vitrectomy systems face prolonged registration cycles and stringent approval processes.
This demonstrates that beyond mere functional integration, successful entry into this field requires Chinese manufacturers to master high-precision opto-electro-mechanical-fluidic control technologies while completing full-system validation across algorithms, hardware, consumables, and clinical application. It is no exaggeration to say that the combined phaco-vitrectomy system represents the most technically demanding and systemically complex core equipment in modern ophthalmic operating rooms. This is precisely why the global market has long been dominated by established players such as Alcon, Zeiss, Bausch + Lomb, BVI, and Oertli.
So why, after years of relative quiet, has the development of China-made combined phaco-vitrectomy systems suddenly gained momentum at this particular juncture?
The maturation of any industrial sector is never instantaneous; it requires the convergence of enabling conditions—technological readiness, market opportunity, and strategic investment.
This alignment is now emerging in China's market for combined phaco-vitrectomy systems. Several factors are creating a pivotal window for domestic contenders: Chinese manufacturers have reached a critical level of proficiency in core technologies such as ultrasonic energy delivery, infusion control, and vitreous cutting drives. This technical progress is further amplified by talent mobility from multinational corporations, supportive government procurement policies favoring local innovation, and growing venture capital interest.
A significant demand driver is the pressing need for advanced surgical equipment upgrades across China's secondary and tertiary hospitals, which substantially expands the addressable market for these locally developed platforms.
Based on public disclosures, VCBeat has mapped the key players and products currently developing combined phaco-vitrectomy systems in China:
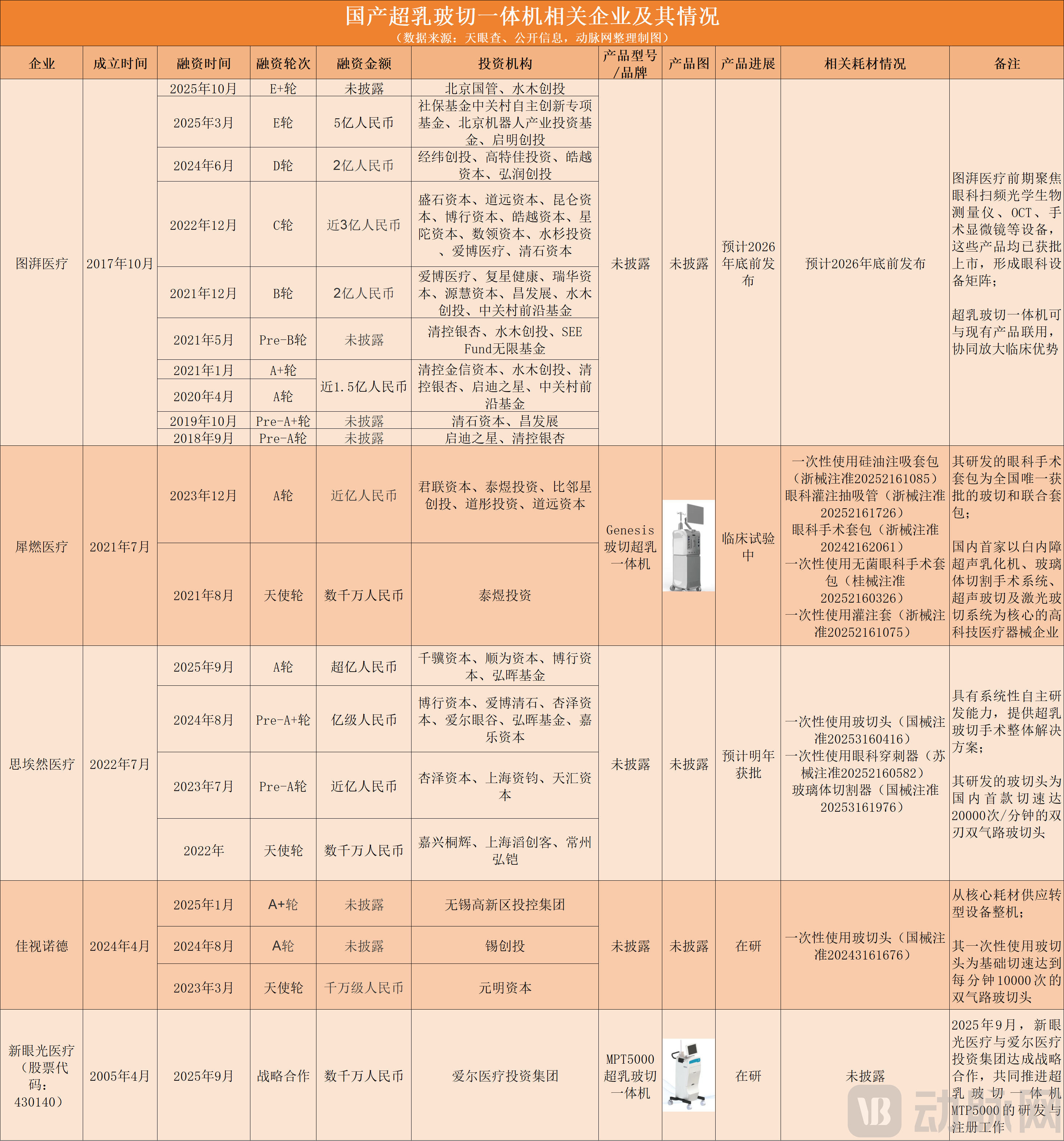
Chinese companies related to combined phaco-vitrectomy systems, data compiled and charted by VCBeat
Based on the development progress of various products, a wave of regulatory approvals is anticipated within the next 1-2 years in China. However, the real competition is only just beginning.
Sector investors note that combined phaco-vitrectomy systems represent the most critical equipment in ophthalmic surgery after femtosecond laser systems. While long-term dominance by international brands has created clear potential for domestic substitution, the high complexity and inherent risks of vitreoretinal procedures make clinicians particularly sensitive to device stability and usability. Even after regulatory clearance is obtained, the absence of large-scale clinical data demonstrating safety and efficacy will likely prevent explosive growth. Market penetration is expected to follow a more gradual trajectory of "iterative optimization and phased adoption."
Wang Yingqi, co-founder of TowardPi Medical, also emphasizes that regulatory approval does not represent the decisive milestone for surgical devices. "Vitrectomy systems can pursue the clinical evaluation pathway, making their registration timeline relatively predictable. However, the true determinants of user adoption are product performance, maturity, usability, and system stability," he notes. "Even if several companies obtain approvals within the next year or two, it doesn't automatically translate to immediate, large-scale hospital adoption. Product refinement requires continued iteration, and I believe a more realistic timeline for meaningful market penetration is two to three years."
It should be noted that while the next 1-2 years represent a concentrated product launch window, only a handful of Chinese manufacturers currently possess true mass-production capabilities. The sector's breakthrough will depend not on a sudden surge in product variants, but on the alignment of clinical acceptance and policy direction.
A significant shift is occurring at the national level, where the "domestic-first" procurement policy is evolving from guidance into quantifiable mandates. Chinese public hospital tenders now commonly include specific procurement quotas for domestic equipment. Recent regulations further stipulate that simple assembly, packaging, or labeling by foreign companies within China no longer qualifies as domestic production—core supply chains must remain in China, with clearly defined localization metrics. With these policy boundaries established, hospital procurement is inevitably shifting toward local manufacturers with genuine independent R&D and manufacturing capabilities.
Against this backdrop, Sierra Medical has garnered significant industry attention following its successful product launch and financing rounds. The company's prominence stems not only from being one of the few domestic players with systematic in-house R&D capabilities, but also from its sustained commitment to substantial research investment.
Among multiple industry experts interviewed by VCBeat, most indicated that the domestic substitution pathway for combined phaco-vitrectomy systems in China is beginning with consumables.
"For manufacturers, selling the console is just the beginning of the business relationship," one industry insider noted. Compared to the one-time sale of equipment, sustained profitability primarily comes from subsequent purchases of high-value consumables such as surgical procedure packs, vitreous cutters, and micro-incision blades.
Taking procedure packs as an example—which typically include phaco handpiece needles, I/A tubing, fluid collection bags, seals, and gaskets—these essentially function as disposable "surgical ammunition crates." Each procedure requires a fresh pack that is loaded pre-surgery and discarded post-operation. Without these packs, the surgical system cannot establish the irrigation-aspiration circuit, rendering the procedure impossible. Current Chinese hospital pricing places Alcon's packs at approximately CNY 4,000–5,000 per unit, Bausch + Lomb's at CNY 3,000–4,000, while entry-level brands range between CNY 2,000–3,000. While widespread equipment replacement remains in progress, the substitution potential within the consumables market presents a more immediate and substantial opportunity.
Taking vitreous cutters as another example: these components are inserted directly into the eyeball during surgery to perform high-speed cutting of pathological vitreous, making them critical to both procedural safety and efficiency. Higher cutting speeds enable greater surgical precision while minimizing traction and potential damage to the retina. Although classified as Class III medical devices, vitreous cutters are included in China's NMPA catalog of devices exempt from clinical evaluation, allowing manufacturers to navigate regulatory pathways more efficiently.
Against the backdrop of ongoing healthcare cost containment policy, practical realities at the hospital level are further reinforcing this trend. "Under cost control policy pressures, many Chinese hospitals are operating vitreoretinal surgery departments on thin margins. The availability of locally produced consumables will significantly alleviate this financial pressure," explained one industry source. "This economic reality makes the consumables segment the logical starting point for domestic substitution."
Current market developments confirm that consumables are indeed spearheading the localization of combined phaco-vitrectomy systems in China.
A case in point is the ophthalmic surgical procedure pack (Zhejiang Medical Device Registration NO 20242162061) developed by Xiran Health, which recently received market approval. The product—comprising tubing, fluid collection cassette assemblies, aspiration tubes, drainage tubes, along with optional test chambers and infusion sets—is specifically indicated for establishing irrigation and aspiration pathways during phacoemulsification, vitrectomy, and combined procedures. It currently holds the distinction of being the only approved procedure pack compatible with both standalone vitrectomy and combined phaco-vitrectomy surgeries in China.
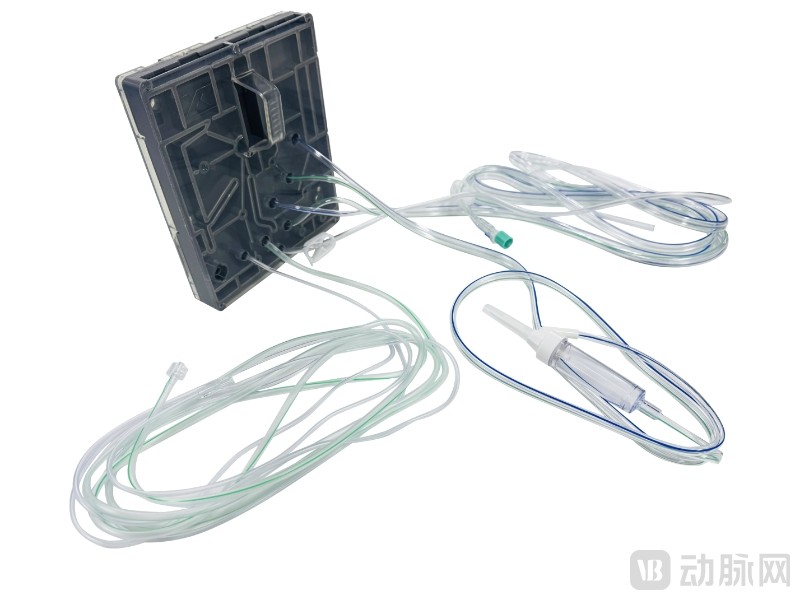

The ophthalmic surgical procedure pack developed by Xiran Health
In the vitreous cutter segment, Sierra Medical's NEXVIT® 20K CPM disposable vitreous cutter represents China's first domestically produced dual-blade, dual-pneumatic system capable of reaching 20,000 cuts per minute. This high-speed cutting technology significantly reduces intraoperative retinal traction risk while enhancing both procedural safety and surgical efficiency. The product line offers comprehensive clinical flexibility through 23G, 25G and 27G gauge options with dual cutting speeds of 10,000 CPM and 20,000 CPM, maintaining compatibility with mainstream surgical platforms to address diverse surgical requirements.
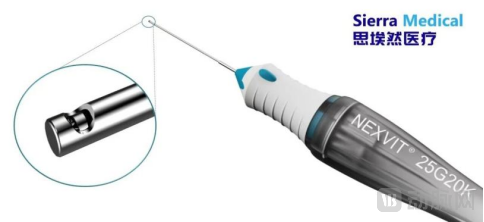
Sierra Medical's NEXVIT® 20K CPM disposable vitreous cutter
Brisight Nord represents another noteworthy contender in this space. Its independently developed disposable vitreous cutter (NMPA Registration NO 20243161676) holds dual significance as China's first domestically developed vitreous cutter and the world's second dual-pneumatic system achieving a base cutting speed of 10,000 CPM. The product line spans 23G, 25G and 27G gauges with cutting speeds covering 2,500, 5,000, 7,500 and 10,000 CPM, while maintaining compatibility with major vitrectomy systems.
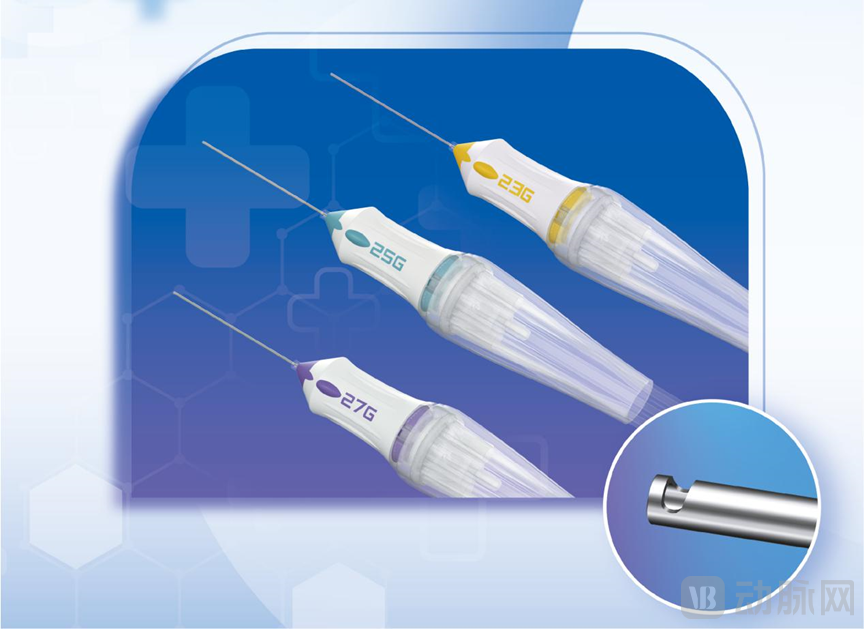
Brisight Nord's dual-pneumatic system high-speed vitreous cutter
While no domestic system has yet received full regulatory approval for market launch, several Chinese companies have demonstrated clear product roadmaps and technical breakthroughs, indicating that market entry is imminent.
Zhang Chi, founder of Xiran Health, revealed that the company's self-developed combined phaco-vitrectomy system, Genesis, features a completely new design benchmarked against parameter standards of leading international brands. The system demonstrates performance comparable to international counterparts while surpassing them in intraocular pressure control and light source design. Currently in clinical trials, the device is expected to gain regulatory approval within the year. Participating surgeons report stable performance across infusion, vacuum, cutting, and system responsiveness, with particularly positive feedback regarding the footpedal response speed and overall operational convenience.
Wang Yingqi, co-founder of TowardPi Medical, indicated that the company's combined phaco-vitrectomy system in development targets the premium market segment. Through both proprietary R&D and strategic technical partnerships, the system has achieved the performance and stability benchmarks required to compete in this high-end segment. Furthermore, TowardPi plans to integrate the vitrectomy system with its existing portfolio of surgical microscopes, biometers, and intraoperative navigation systems, creating a unified surgical ecosystem that enables advanced functionalities such as real-time visualized surgical guidance.
Sierra Medical has achieved notable product differentiation within China's vitrectomy landscape. As one of the few Chinese companies possessing full in-house R&D and manufacturing capabilities across the complete vitrectomy product spectrum, its offerings span console systems, trocars, multi-gauge vitreous cutters, fluidics tubing, light fibers, laser probes, silicone oil infusion lines, and reusable instruments—covering the entire chain of core components. Building on this comprehensive foundation, the company provides surgically tailored procedure packs in various configurations. This integrated approach enables Sierra Medical to deliver a true "comprehensive surgical solution," allowing hospitals to avoid multi-brand sourcing and manual component assembly, thereby better addressing practical needs across clinical operation, procurement management, and billing compliance.
While these Chinese manufacturers have made substantial progress in research and development, it is crucial to recognize that competition in combined phaco-vitrectomy systems depends not on individual specifications, but on overall system performance. The premium nature of a system is fundamentally reflected in its precise tactile feedback and consistent system response—specifically, the accuracy of its recording and feedback mechanisms, its ability to provide what surgeons describe as "smoothness" and "control," and its capacity to maintain consistent stability throughout surgical procedures. These elements collectively determine a system's clinical usability, which explains why combined phaco-vitrectomy systems cannot be evaluated like OCT microscopes based primarily on hardware specifications. Their value derives instead from the comprehensive optimization of system integration, reliability, and clinical experience.
Regulatory approval marks merely the initial step. On the path from product availability to widespread clinical adoption, domestic Chinese manufacturers still face a series of practical challenges.
The first lies in the entrenched market structure and the concentration of surgical volumes. According to Frost & Sullivan analysis, China's vitrectomy procedures exceeded 400,000 cases in 2023, with combined phaco-vitrectomy system installations surpassing 400 units. Publicly available bidding data from Chinese public hospitals, however, records only 65 units. This procurement data reveals Alcon's Constellation series as the market leader with a dominant 47.9% revenue share, followed by Bausch + Lomb at 29.6%, BVI ranking third with 16.1%, and Oertli capturing 6.4% of the market.
The second challenge lies not in market demand, but in surgical capacity. Vitrectomy represents the most skill-dependent procedure in ophthalmology—classified as Level 4 surgery—with only a limited number of Chinese surgeons qualified to perform it independently. Consequently, procedure volumes face structural constraints, particularly in grassroots hospitals. Wang Yingqi, co-founder of TowardPi Medical, analyzes: "Future growth in the vitrectomy market will likely remain steady rather than explosive, with the primary constraint being the surgeon pool. While vitrectomy cutter and procedure pack sales drive revenue, procedure volume ultimately depends on the number of surgeons capable of performing these complex operations. Unless surgical robotics or AI assistance becomes widely adopted, overall procedure growth will remain gradual."
Furthermore, potential price competition from international brands presents another hurdle. As combined phaco-vitrectomy systems essentially function as consumable-driven platforms where core profitability depends on recurring sales of high-margin consumables, international manufacturers maintain significant pricing flexibility. In other words, should domestic alternatives enter the market, established players could deploy strategic price reductions to slow the substitution process.
However, Wang Yingqi believes this does not pose a fundamental threat to Chinese brands: "Under China's 'domestic substitution' policy direction, hospitals will often prioritize domestically manufactured equipment as long as its performance and stability are comparable to imported products. We have already witnessed this trend in the market performance of TowardPi's OCT systems, microscopes, biometers, and cameras. If domestic products offer competitive performance, they can rapidly enter the market and engage in head-to-head competition with international brands."
Despite these challenges, industry participants widely believe the narrative of China's combined phaco-vitrectomy systems is just beginning. Driven by the combined forces of capital, policy, and technology, the sector is approaching a tipping point—transitioning from isolated technological breakthroughs to systematic innovation, and from localized substitution to global competition. Looking ahead, companies are starting to confront a more strategic question: what comes next for combined phaco-vitrectomy systems?
Zhang Chi, founder of Xiran Health, believes that as a core ophthalmic surgical platform, the technological evolution of combined phaco-vitrectomy systems is progressing toward less invasive procedures, higher efficiency, and enhanced surgical safety. These trends manifest specifically through performance optimizations in both core modules: phacoemulsification incisions are becoming smaller with reduced energy delivery, while vitrectomy achieves higher cutting speeds and efficiency, leading to shorter procedural times.
Wang Yingqi, co-founder of TowardPi Medical, offers a complementary perspective: while individual technical specifications continue to advance, achieving significant differentiation will require seamless integration with other diagnostic and surgical equipment. Using TowardPi's own ecosystem as an example, he notes their vitrectomy system is designed to operate alongside the company's biometers and microscopes—particularly their surgical navigation microscopes, which are already being adopted in numerous hospitals. Through such integration, the combined system enables visualized navigation during surgery, with future potential for incorporation into robotic-assisted procedures. Consequently, once performance and reliability benchmarks are met, competition will increasingly focus on delivering comprehensive solutions for vitreoretinal and cataract surgery rather than on standalone device specifications.
Yang Jianxin, founder of Brisight Nord, observes that vitrectomy systems and cutters are evolving toward smaller gauges and higher cutting speeds. This trend not only enhances procedural safety and efficiency while expanding the indications for surgical intervention—bringing treatment possibilities to more patients with vitreoretinal conditions—but also elevates the technical requirements for developing advanced systems.
The emergence of domestically produced combined phaco-vitrectomy systems in China represents more than product innovation; it signifies a restructuring of the core equipment landscape in ophthalmic operating rooms. While technological barriers persist and market maturation remains a long-term endeavor, the industry has reached an inflection point. The next phase of competition will shift from "can it be built?" to "can it be effectively deployed?" Only when these systems prove their worth in real-world surgical settings will China's combined phaco-vitrectomy systems truly fill the longstanding gap in its medical technology landscape.
