The world's first highly selective HER2 TKI, Zongaitinib, approved in China, ushers in a new era for HER2-mutated NSCLC treatment

On August 29, 2025, Boehringer Ingelheim and Sino Biopharmaceutical jointly announced that their innovative drug Zongertinib (BI1810631) has received conditional approval from the China National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). It is indicated as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring HER2 (ERBB2) activating mutations who have previously received at least one systemic therapy. The approval of Zongertinib marks a milestone in the treatment of HER2-mutant NSCLC. It not only addresses the gap in oral targeted therapies for HER2-mutant NSCLC in China but also brings new hope to a broad population of Chinese patients with HER2-mutant NSCLC. This development is expected to reshape the current diagnostic and treatment landscape and usher in a new era of precision medicine
Unmet need: Treatment of HER2-mutant NSCLC urgently requires
The incidence of HER2 mutations in NSCLC is approximately 2%-4%, and among the many known driver genes, HER2 mutations have consistently been regarded as one of the "difficult-to-treat subtypes[1]HER2-mutant NSCLC is more common in female patients, non-smokers, those with lung adenocarcinoma, and younger individuals, and is often associated with a higher risk of brain metastasis and poor[2, 3]。
For a long time, patients with advanced NSCLC harboring HER2 mutations have faced significant and unmet treatment needs. Traditional chemotherapy and immunotherapy have shown limited efficacy in the HER2-mutant population[4]. Although some pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have shown certain activity in NSCLC patients with HER2 mutations, they are often accompanied by significant EGFR-related toxicities such as diarrhea and skin rash, which limit their clinical application[1]Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have shown some efficacy in this field, but they require intravenous administration and carry the risk of potential adverse events such as bone marrow suppression and interstitial lung disease[1, 5]. Therefore, there is an urgent need for an efficient, safe, and orally convenient novel HER2-targeted therapy to improve the quality of life and prognosis of patients with advanced HER2-mutated NSCLC
Precision-Guided: Highly Selective HER2 TKI, Innovative Mechanism Revolutionizes Treatment
Zongaitinib is a novel oral, highly selective HER2 TKI. Its molecular structure contains an acrylamide group that can form an irreversible covalent bond with HER2 cysteine 805 (Cys805), enabling efficient and precise targeting of both wild-type (WT) and mutant HER2. This inhibits their phosphorylation and the activation of downstream signaling pathways, thereby suppressing tumor cell proliferation and survival, without affecting the signaling transduction of wild-type EGFR (Figure [6]. The high selectivity of zongetini for HER2 demonstrates significant potential in combating HER2-mutant NSCLC.

Figure 1 Mechanism of Action of Zongait[7]
Data speaks: Balancing efficacy and safety, significantly improving patient outcomes
The approval of Zongaitini is based on the positive results from its pivotal Beamion LUNG-1 study (Figure 2).
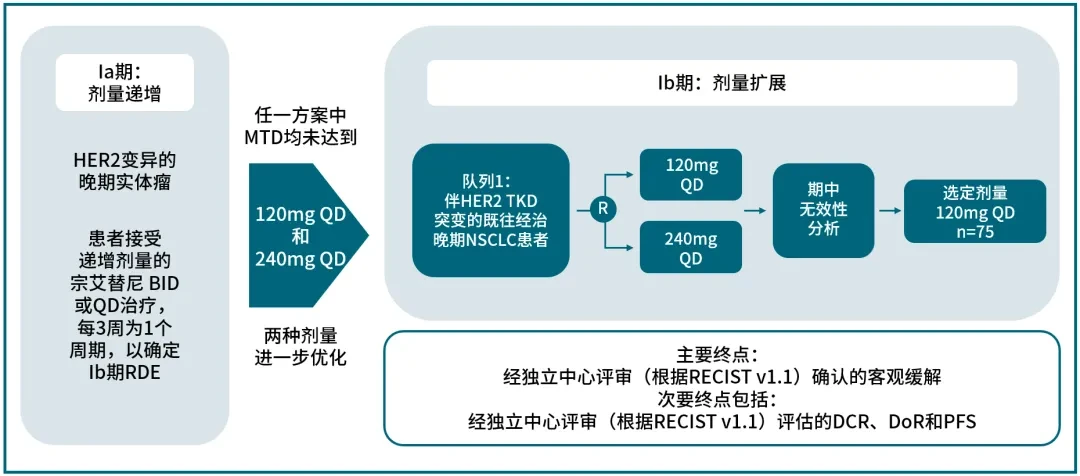
Figure 2: Beamion LUNG-1 Study Design[8]
In April 2025, the world's leading medical journal *The New England Journal of Medicine* (NEJM) published the core findings of the Phase Ib trial of the Beamion LUNG-1 study[1]. The study results showed that among previously treated non-squamous NSCLC patients with HER2 TKD mutations (Cohort 1), a total of 75 patients received 120 mg of zongaitinib once daily. As of the data cutoff date (November 29, 2024The objective response rate (ORR) confirmed by a blinded independent central review (IRC) was as high as 71%.(95% CI 60%-80%), with a complete response (CR) rate of 7% and a partial response (PR) rate of 64%,Disease control rate (DCR) was as high as 96% (95% CI 89%-99(Table 1This means that the condition of the vast majority of patients has been effectively controlled. Particularly encouraging is,Patients who achieved remission experienced durable and stable efficacy, with a median duration of remission (DoR) as long as 14.1(95% CI: 6.9–NE).The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 12.4(95% CI: 8.2–NE) (Figure 3
Table 1 Response Outcomes of Patients in Cohort 1 Receiving 120 mg Zongaitinib Treatment[1]
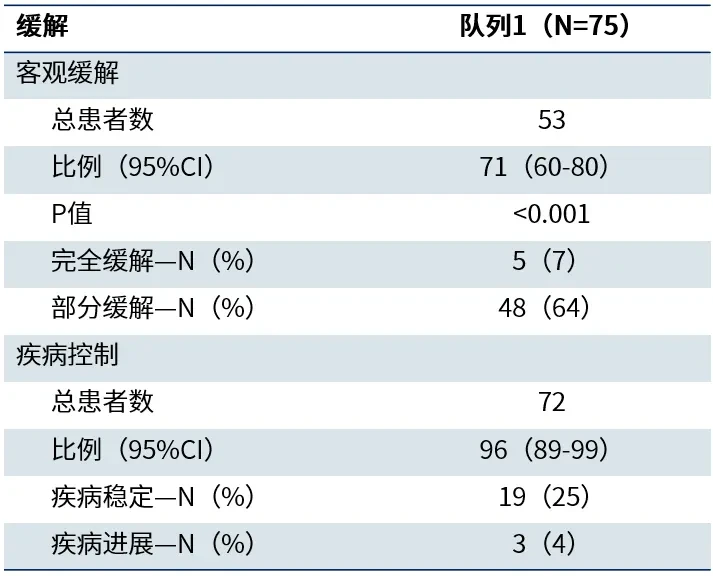
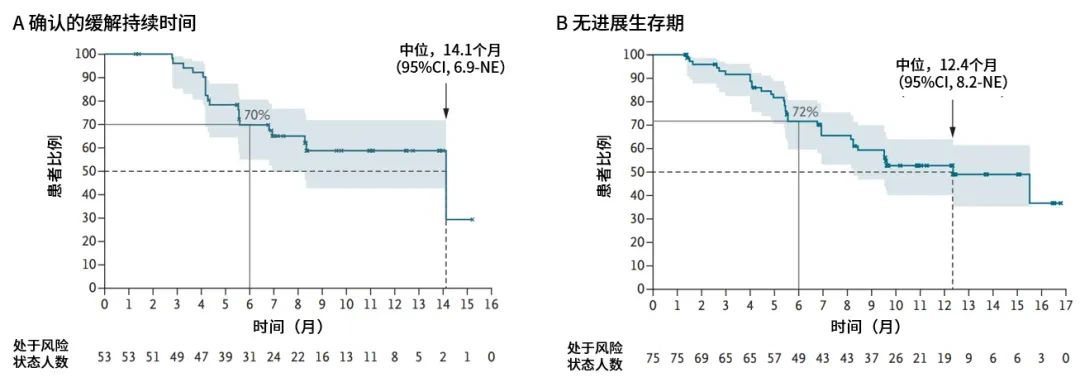
Figure 3: Efficacy of Beamion LUNG-1 Study Cohort 1[1]
Regardless of the patient's gender, age, prior treatment, ethnicity, mutation type, and brain metastasis status, responses were observed across all patient subgroups. In the common A775_G776insYVMA mutation subgroup, the ORR was as high as 81%. It is worth noting that,In patients with baseline brain metastases (accounting for 37%), the systemic ORR reached 64%, and the intracranial ORR also achieved 41%.These data fully demonstrate that zong'aitinib can effectively control brain metastasis lesions, providing comprehensive treatment benefits for
In terms of safety, zong'aitinib was generally well[1]。In queue 1The incidence of grade ≥3 treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) was only 17%.Mainly alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation (8%) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) elevation (5%). These adverse events are usually reversibleDiscontinuation of treatment due to adverse events (3%) or dose reduction (7%) was。Since zongaitinib retains the function of wild-type EGFR, the incidence of EGFR-related toxicity is relativelyThe most common adverse events, diarrhea (56%) and rash (33%), were mostly grade 1-2, with only one patient experiencing grade 3 diarrhea. AdditionallyNo drug-related interstitial lung disease events were reported.. This "efficient and safe" therapeutic advantage provides a solid guarantee for patients to achieve longer-term and more stable treatment.
Milestone Moment: U.S. and China Approve in Quick Succession, Bringing Rapid Benefits to Chinese
Zongaitinib has achieved multiple breakthroughs in its drug development and regulatory approval process. In 2023, it was granted Fast Track designation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) due to its potential clinical advantages. In 2024, it received Breakthrough Therapy designations from both the U.S. FDA and the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA). In January 2025, its marketing application in China was accepted and included in the priority review process. On August 8 of the same year (U.S. local time), Zongaitinib received accelerated approval from the U.S. FDA, and less than a month later, it was granted conditional approval by China's NMPA.
The approval of zongaitinib in China marks the first time that Chinese patients with HER2-mutated NSCLC have access to a highly selective, precise, and oral targeted treatment option, filling the gap in local oral targeted therapies and truly achieving "synchronization with the globe and acceleration for patients." Furthermore, zongaitinib has received high recognition from both domestic and internationalIn April of this year, Zongaitinib was included in the 2025 CSCO NSCLC Diagnosis and Treatment[9], In August, the NCCN Guidelines were updated again: for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (2025.V8), zongetitinib has been added as the preferred subsequent treatment option for patients with HER2-mutant advanced or metastatic NSCLC who have previously received systemic therapy.[10]。The authoritative guidelines' recommendations provide a solid foundation and strong support for the clinical application of Zongait
In the future, the exploration of zongaitinib in the treatment of HER2-mutated NSCLC is far from over. On August 19, zongaitinib once again received the "Breakthrough Therapy" designation from the CDE for the first-line treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC harboring HER2 TKD activating mutations. Beamion LUNG-2 (NCT06151574) is a Phase III clinical study evaluating the efficacy and safety of zongaitinib as a first-line treatment versus standard therapy in patients with unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic HER2-mutated NSCLC[1]。
The approval of Zongaitinib marks a significant breakthrough in the precision treatment of lung cancer, extending from survival benefits to improvements in quality of life. Driven by an innovative mechanism, this therapeutic revolution will bring new hope to Chinese HER2-mutated NSCLC patients in their fight against cancer. It is hoped that this innovative drug will benefit more patients in China in the
